Evaluation of the Causes of Erectile Dysfunction in Patients Undergoing Penile Doppler Ultrasonography in Pakistan
- PMID: 28459144
- PMCID: PMC5419116
- DOI: 10.5534/wjmh.2017.35.1.22
Evaluation of the Causes of Erectile Dysfunction in Patients Undergoing Penile Doppler Ultrasonography in Pakistan
Abstract
Purpose: In patients with erectile dysfunction, it is important to differentiate psychogenic from organic causes. Penile Doppler ultrasonography is a relatively inexpensive and minimally invasive tool for this purpose. This study was conducted to evaluate the causes of erectile dysfunction in an adult male population, using penile Doppler ultrasonography.
Materials and methods: A retrospective study was conducted in a single center. All patients who presented with complaints of erectile dysfunction and underwent penile Doppler ultrasonography between July 2014 and June 2016 were included in this study. All examinations were performed using GE Voluson S6 and GE Logiq P5 devices. Following baseline scans, an intracavernosal injection of 20 μg of prostaglandin E1 was given. Peak systolic and end diastolic velocities were measured in each cavernosal artery. Patients with a peak systolic velocity of <25 cm/s were considered to have arterial insufficiency, while an end diastolic velocity of >5 cm/s was considered to indicate venous incompetence.
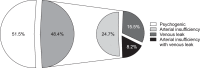
Results: Out of 97 patients (mean age, 37.09±11.59 years; range, 19~69 years), 50 patients (51.5%) had normal findings, 24 patients (24.7%) had arterial insufficiency, 15 patients (15.5%) had a venous leak, and 8 patients (8.2%) patients had arterial insufficiency with a venous leak. Psychogenic erectile dysfunction was significantly higher among patients aged ≤40 years, while arterial insufficiency with or without a venous leak was significantly higher among patients aged >40 years (p=0.022).
Conclusions: A majority of the studied individuals demonstrated no organic cause of erectile dysfunction, thus confirming a high prevalence of the psychogenic etiology, particularly in relatively young individuals.
Keywords: Doppler, color; Impotence, vasculogenic; Ultrasonography.
Copyright © 2017 Korean Society for Sexual Medicine and Andrology
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Diagnostic categorization of erectile dysfunction using duplex color doppler ultrasonography and significance of phentolamine redosing in abolishing false diagnosis of venous leak impotence: A single center experience.Indian J Radiol Imaging. 2020 Jul-Sep;30(3):344-353. doi: 10.4103/ijri.IJRI_419_19. Epub 2020 Oct 15. Indian J Radiol Imaging. 2020. PMID: 33273769 Free PMC article.
-
Pharmaco Penile Duplex Ultrasonography in the Evaluation of Erectile Dysfunction.J Clin Diagn Res. 2017 Jan;11(1):TC07-TC10. doi: 10.7860/JCDR/2017/25092.9270. Epub 2017 Jan 1. J Clin Diagn Res. 2017. PMID: 28274021 Free PMC article.
-
Color Doppler sonography in the evaluation of erectile dysfunction: patterns of temporal response to papaverine.AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1991 Aug;157(2):331-6. doi: 10.2214/ajr.157.2.1853817. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1991. PMID: 1853817
-
Color Doppler sonography in the evaluation of erectile dysfunction.Radiographics. 1992 Jan;12(1):3-17; discussion 18-9. doi: 10.1148/radiographics.12.1.1734478. Radiographics. 1992. PMID: 1734478 Review.
-
A Critical Analysis of Methodology Pitfalls in Duplex Doppler Ultrasound in the Evaluation of Patients With Erectile Dysfunction: Technical and Interpretation Deficiencies.J Sex Med. 2020 Aug;17(8):1416-1422. doi: 10.1016/j.jsxm.2020.05.023. Epub 2020 Jul 3. J Sex Med. 2020. PMID: 32631763 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Diagnostic categorization of erectile dysfunction using duplex color doppler ultrasonography and significance of phentolamine redosing in abolishing false diagnosis of venous leak impotence: A single center experience.Indian J Radiol Imaging. 2020 Jul-Sep;30(3):344-353. doi: 10.4103/ijri.IJRI_419_19. Epub 2020 Oct 15. Indian J Radiol Imaging. 2020. PMID: 33273769 Free PMC article.
-
Factors Associated With Erectile Dysfunction in Men: A Cross-Sectional Study From Balochistan, Pakistan.Cureus. 2025 Jan 4;17(1):e76928. doi: 10.7759/cureus.76928. eCollection 2025 Jan. Cureus. 2025. PMID: 39764481 Free PMC article.
-
Finasteride and Erectile Dysfunction in Patients with Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia or Male Androgenetic Alopecia.World J Mens Health. 2019 May;37(2):157-165. doi: 10.5534/wjmh.180029. Epub 2018 Aug 10. World J Mens Health. 2019. PMID: 30209896 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Doppler Ultrasonographic Evaluation of Erectile Dysfunction in a Northern Nigerian Tertiary Hospital.J West Afr Coll Surg. 2023 Oct-Dec;13(4):93-97. doi: 10.4103/jwas.jwas_71_23. Epub 2023 Sep 16. J West Afr Coll Surg. 2023. PMID: 38449545 Free PMC article.
-
Randomized Placebo Controlled Trial of Sildenafil Citrate, Cognitive Behavior Sex Therapy and Integrated Treatment in Men Diagnosed With Non Organic Erectile Dysfunction.Sex Med. 2022 Feb;10(1):100464. doi: 10.1016/j.esxm.2021.100464. Epub 2021 Dec 16. Sex Med. 2022. PMID: 34922302 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Juszczak K, Wyczółkowski M, Filipek M, Thor PJ. Pathophysiology of erectile dysfunction in men. Folia Med Cracov. 2008;49:67–77. - PubMed
-
- Shamloul R, Ghanem H. Erectile dysfunction. Lancet. 2013;381:153–165. - PubMed
-
- Hatzimouratidis K, Eardley I, Giuliano F, Moncada I, Salonia A. Guidelines on male sexual dysfunction: erectile dysfunction and premature ejaculation. Arnhem: European Association of Urology; 2015. - PubMed
-
- Johannes CB, Araujo AB, Feldman HA, Derby CA, Kleinman KP, McKinlay JB. Incidence of erectile dysfunction in men 40 to 69 years old: longitudinal results from the Massachusetts male aging study. J Urol. 2000;163:460–463. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous