EGFR and HER2 activate rigidity sensing only on rigid matrices
- PMID: 28459445
- PMCID: PMC5920513
- DOI: 10.1038/nmat4893
EGFR and HER2 activate rigidity sensing only on rigid matrices
Abstract
Epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) interacts with integrins during cell spreading and motility, but little is known about the role of EGFR in these mechanosensing processes. Here we show, using two different cell lines, that in serum- and EGF-free conditions, EGFR or HER2 activity increase spreading and rigidity-sensing contractions on rigid, but not soft, substrates. Contractions peak after 15-20 min, but diminish by tenfold after 4 h. Addition of EGF at that point increases spreading and contractions, but this can be blocked by myosin-II inhibition. We further show that EGFR and HER2 are activated through phosphorylation by Src family kinases (SFK). On soft surfaces, neither EGFR inhibition nor EGF stimulation have any effect on cell motility. Thus, EGFR or HER2 can catalyse rigidity sensing after associating with nascent adhesions under rigidity-dependent tension downstream of SFK activity. This has broad implications for the roles of EGFR and HER2 in the absence of EGF both for normal and cancerous growth.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures
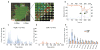
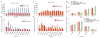
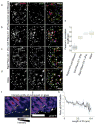
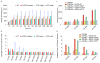
Comment in
-
EGFR probes matrix stiffness.Nat Cell Biol. 2017 May 31;19(6):600. doi: 10.1038/ncb3550. Nat Cell Biol. 2017. PMID: 28561056 No abstract available.
References
-
- Wang HB, Dembo M, Wang YL. Substrate flexibility regulates growth and apoptosis of normal but not transformed cells. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2000;279:C1345–1350. - PubMed
-
- Engler AJ, Sen S, Sweeney HL, Discher DE. Matrix elasticity directs stem cell lineage specification. Cell. 2006;126:677–89. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

