Topo-phylogeny: Visualizing evolutionary relationships on a topographic landscape
- PMID: 28459802
- PMCID: PMC5411050
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0175895
Topo-phylogeny: Visualizing evolutionary relationships on a topographic landscape
Abstract
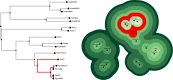
Phylogenetic trees are the de facto standard for visualizing evolutionary relationships, but large trees can be difficult to interpret because they require a high cognitive load to identify relationships between multiple operational taxonomic units (OTUs). We present a new tool for displaying phylogenetic relationships as a topographic map in which OTUs autonomously attract or repel one another based on their individual branch lengths and distance to a common ancestor. This data visualization paradigm makes it possible to preattentively identify the nature of the relationship between items without having to trace a complex network of branches back to the root. This tool was developed for exploring phylogenetic data, but the technique could be extended for visualizing other hierarchical structures as well.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures



References
-
- Carrizo SF. Phylogenetic Trees: An Information Visualisation Perspective. In: Proceedings of the Second Conference on Asia-Pacific Bioinformatics—Volume 29 [Internet]. Darlinghurst, Australia, Australia: Australian Computer Society, Inc.; 2004 [cited 2014 Oct 27]. p. 315–320. (APBC ‘04). Available from: http://dl.acm.org/citation.cfm?id=976520.976563
-
- Munzner T, Guimbretière F, Tasiran S, Zhang L, Zhou Y. TreeJuxtaposer: Scalable Tree Comparison Using Focus+Context with Guaranteed Visibility. In: ACM SIGGRAPH 2003 Papers [Internet]. New York, NY, USA: ACM; 2003 [cited 2014 Oct 29]. p. 453–462. (SIGGRAPH ‘03).
-
- Rost U, Bornberg-Bauer E. TreeWiz: interactive exploration of huge trees. Bioinformatics. 2002. January 1;18(1):109–14. - PubMed
-
- Huson DH, Richter DC, Rausch C, Dezulian T, Franz M, Rupp R. Dendroscope: An interactive viewer for large phylogenetic trees. BMC Bioinformatics. 2007;8:460 doi: 10.1186/1471-2105-8-460 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

