Minichromosome maintenance protein 2 and 3 promote osteosarcoma progression via DHX9 and predict poor patient prognosis
- PMID: 28460433
- PMCID: PMC5432265
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.15474
Minichromosome maintenance protein 2 and 3 promote osteosarcoma progression via DHX9 and predict poor patient prognosis
Abstract
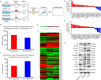
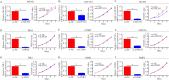
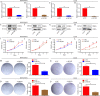
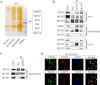
A label free quantitative proteomic approach (SWATH™ experiment) was performed to identify tumor-associated nuclear proteins that are differentially expressed between osteosarcoma cells and osteoblast cells. By functional screening, minichromosome maintenance protein 2 (MCM2) and minichromosome maintenance protein 3 (MCM3) were found to be related to osteosarcoma cell growth. Here, we show that knockdown of MCM2 or MCM3 inhibits osteosarcoma growth in vitro and in vivo. In co-immunoprecipitation and co-localization experiments, MCM2 and MCM3 were found to interact with DExH-box helicase 9 (DHX9) in osteosarcoma cells. A rescue study showed that the decreased growth of osteosarcoma cells by MCM2 or MCM3 knockdown was reversed by DHX9 overexpression, indicating that MCM2 and MCM3 activity was DHX9-dependent. In addition, the depletion of DHX9 hindered osteosarcoma cell proliferation. Notably, MCM2 and MCM3 expression levels were positively correlated with the DHX9 expression level in tumor samples and were associated with a poor prognosis in patients with osteosarcoma. Taken together, these results suggest that the MCM2/MCM3-DHX9 axis has an important role in osteosarcoma progression.
Keywords: DHX9; MCM2; MCM3; osteosarcoma; proliferation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- Shahbazi J, Scarlett CJ, Norris MD, Liu B, Haber M, Tee AE, Carrier A, Biankin AV, London WB, Marshall GM, Lock RB, Liu T. Histone deacetylase 2 and N-Myc reduce p53 protein phosphorylation at serine 46 by repressing gene transcription of tumor protein 53-induced nuclear protein 1. Oncotarget. 2014;5:4257–68. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.1991. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

