Early outcome of early-goal directed therapy for patients with sepsis or septic shock: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials
- PMID: 28460438
- PMCID: PMC5432353
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.15550
Early outcome of early-goal directed therapy for patients with sepsis or septic shock: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials
Abstract
Various trials and meta-analyses have reported conflicting results concerning the application of early goal-directed therapy (EGDT) for sepsis and septic shock. The aim of this study was to update the evidence by performing a systematic review and meta-analysis. Multiple databases were searched from initial through August, 2016 for randomized controlled trials (RCTs) which investigated the associations between the use of EGDT and mortality in patients with sepsis or septic shock. Meta-analysis was performed using random-effects model and heterogeneity was examined through subgroup analyses. The primary outcome of interest was patient all-cause mortality including hospital or ICU mortality. Seventeen RCTs including 6207 participants with 3234 in the EGDT group and 2973 in the control group were eligible for this study. Meta-analysis showed that EGDT did not significantly reduce hospital or intensive care unit (ICU) mortality (relative risk [RR] 0.89, 95% CI 0.78 to 1.02) compared with control group for patients with sepsis or septic shock. The findings of subgroup analyses stratified by study region, number of research center, year of enrollment, clinical setting, sample size, timing of EGDT almost remained constant with that of the primary analysis. Our findings provide evidence that EGDT offers neutral survival effects for patients with sepsis or septic shock. Further meta-analyses based on larger well-designed RCTs or individual patient data meta-analysis are required to explore the survival benefits of EDGT in patients with sepsis or septic shock.
Keywords: early-goal directed therapy; meta-analysis; randomized controlled trial; sepsis; septic shock.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no potential conflicts of interest.
Figures
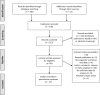

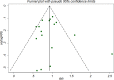
Similar articles
-
Effect of early goal directed therapy in the treatment of severe sepsis and/or septic shock.Curr Med Res Opin. 2016 Nov;32(11):1773-1782. doi: 10.1080/03007995.2016.1206872. Epub 2016 Sep 9. Curr Med Res Opin. 2016. PMID: 27348416
-
High-volume haemofiltration for sepsis in adults.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Jan 31;1(1):CD008075. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD008075.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. PMID: 28141912 Free PMC article.
-
Systemic pharmacological treatments for chronic plaque psoriasis: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Apr 19;4(4):CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 May 23;5:CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub5. PMID: 33871055 Free PMC article. Updated.
-
The efficacy and safety of plasma exchange in patients with sepsis and septic shock: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Crit Care. 2014 Dec 20;18(6):699. doi: 10.1186/s13054-014-0699-2. Crit Care. 2014. PMID: 25527094 Free PMC article.
-
Drugs for preventing postoperative nausea and vomiting in adults after general anaesthesia: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Oct 19;10(10):CD012859. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD012859.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020. PMID: 33075160 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Cost Impact Model of a Novel Multi-mRNA Host Response Assay for Diagnosis and Risk Assessment of Acute Respiratory Tract Infections and Sepsis in the Emergency Department.J Health Econ Outcomes Res. 2020 Apr 29;7(1):24-34. doi: 10.36469/jheor.2020.12637. eCollection 2020. J Health Econ Outcomes Res. 2020. PMID: 32685595 Free PMC article.
-
The value of procalcitonin and brain natriuretic peptide in predicting the prognosis of sepsis.Am J Transl Res. 2023 Mar 15;15(3):1921-1927. eCollection 2023. Am J Transl Res. 2023. PMID: 37056803 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative analysis of the prognosis of fluid resuscitation in sepsis shock patients guided by radial artery applanation tonometry and critical care ultrasound: a retrospective cohort pilot study.BMC Surg. 2025 Jul 3;25(1):262. doi: 10.1186/s12893-025-03000-w. BMC Surg. 2025. PMID: 40611055 Free PMC article.
-
Septic shock in the ER: diagnostic and management challenges.Open Access Emerg Med. 2019 Apr 11;11:77-86. doi: 10.2147/OAEM.S166086. eCollection 2019. Open Access Emerg Med. 2019. PMID: 31114401 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Rivers E, Nguyen B, Havstad S, Ressler J, Muzzin A, Knoblich B, Peterson E, Tomlanovich M, Early Goal-Directed Therapy Collaborative Group Early goal-directed therapy in the treatment of severe sepsis and septic shock. N Engl J Med. 2001;345:1368–77. - PubMed
-
- Dellinger RP, Levy MM, Rhodes A, Annane D, Gerlach H, Opal SM, Sevransky JE, Sprung CL, Douglas IS, Jaeschke R, Osborn TM, Nunnally ME, Townsend SR, et al. Surviving Sepsis Campaign: international guidelines for management of severe sepsis and septic shock, 2012. Intensive Care Med. 2013;39:165–228. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Dellinger RP, Levy MM, Carlet JM, Bion J, Parker MM, Jaeschke R, Reinhart K, Angus DC, Brun-Buisson C, Beale R, Calandra T, Dhainaut JF, Gerlach H, et al. Surviving Sepsis Campaign: international guidelines for management of severe sepsis and septic shock: 2008. Crit Care Med. 2008;36:296–327. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

