Effect of Statin Therapy on the Progression of Autosomal Dominant Polycystic Kidney Disease. A Secondary Analysis of the HALT PKD Trials
- PMID: 28460625
- PMCID: PMC5688015
- DOI: 10.2174/1573402113666170427142815
Effect of Statin Therapy on the Progression of Autosomal Dominant Polycystic Kidney Disease. A Secondary Analysis of the HALT PKD Trials
Abstract
Background: Autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease (ADPKD) commonly results in end-stage renal disease (ESRD), yet a long-term treatment that is well tolerated is still lacking. In a small randomized trial in children and adolescents pravastatin administration for 3 years was associated with reduced renal cyst growth, but no large trial has tested the effect of statins in adults.
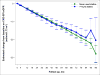
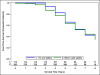
Methods: We performed a post-hoc analysis of the HALT PKD trials to compare outcomes of participants who never used statins with those who used statin for at least 3 years. Because statins were not randomly allocated, we used propensity score models with inverse probability of treatment weighting to account for imbalances between the groups. For subjects in Study A (preserved renal function, n=438) relevant outcomes were percent change in total kidney and liver volume and the rate of decline in estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR); for those in Study B (reduced renal function, n=352) we compared time to the composite endpoint of death, ESRD or 50% decline in eGFR. Follow-up was 5-8 years.
Results: There was no difference in any outcome between the 2 groups. However, limitations of this analysis are the small number of statin users in Study A, different statin drugs and doses used, non-randomized allocation and advanced disease stage in Study B.
Conclusion: Although this post-hoc analysis of the HALT PKD trials does not demonstrate a benefit of statin therapy, conclusions remain preliminary. A larger randomized trial in young people with ADPKD is necessary to answer the question whether statins can slow renal cyst growth and preserve kidney function.
Keywords: Autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease; HALT PKD trials; end-stage renal disease; glomerular filtration rate; hydroxymethylglutaryl-CoA reductase inhibitors; total kidney volume.
Copyright© Bentham Science Publishers; For any queries, please email at epub@benthamscience.org.
Figures




References
-
- Iglesias CG, Torres VE, Offord KP, Holley KE, Beard CM, Kurland LT. Epidemiology of adult polycystic kidney disease, Olmsted County, Minnesota: 1935–1980. Am J Kidney Dis. 1983;2:630–639. - PubMed
-
- Fick-Brosnahan GM, Ecder T, Schrier RW. Polycystic kidney disease. In: Schrier R, editor. Diseases of the Kidney. 7th. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins; Philadelphia, PA: 2001. pp. 547–588.
-
- Torres VE, Harris PC, Pirson Y. Autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease. Lancet. 2007;369:1287–1301. - PubMed
-
- Spithoven EM, Kramer A, Meijer E, et al. Analysis of data from the ERA-EDTA Registry indicates that conventional treatments for chronic kidney disease do not reduce the need for renal replacement therapy in autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease. Kidney Int. 2014;86:1244–1252. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- U01 DK062401/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK090728/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK062402/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR025780/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR001064/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR025752/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR000001/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR001032/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR000135/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR000454/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR000051/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK062411/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR025008/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK062410/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR000585/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR024989/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR000039/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR033179/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR000054/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR023940/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR000439/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK062408/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK044863/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR001082/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR001102/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK082230/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR024150/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR025758/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
