Her2 assessment using quantitative reverse transcriptase polymerase chain reaction reliably identifies Her2 overexpression without amplification in breast cancer cases
- PMID: 28460632
- PMCID: PMC5412048
- DOI: 10.1186/s12967-017-1195-7
Her2 assessment using quantitative reverse transcriptase polymerase chain reaction reliably identifies Her2 overexpression without amplification in breast cancer cases
Abstract
Background: Immunohistochemistry (IHC) and fluorescent-in situ hybridization (FISH) are standard methods to assess human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2) status in breast cancer (BC) patients. Real-time quantitative polymerase-chain-reaction (qRT-PCR) is able to detect HER2 overexpression. Here we compared FISH, IHC, quantitative PCR (qPCR), and qRT-PCR to determine the concordance rates and evaluate their relative roles in HER2 determination.
Patients and methods: We determined HER2 status in 153 BC patients, using IHC, FISH, Q-PCR and qRT-PCR. In discordant cases, we directly measured HER2 protein levels using Western blotting.
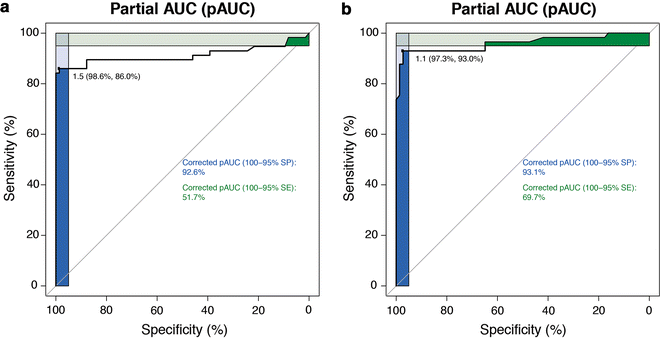
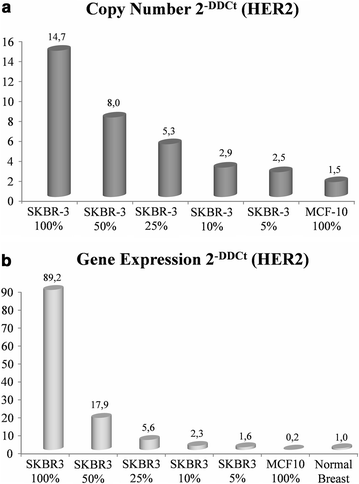
Results: The overall agreement (OA) between FISH and Q-PCR was 94.1, with a k value of 0.87. Assuming FISH as the standard reference, Q-PCR showed an 86.1% sensitivity and a 99.0% specificity with a global accuracy of 91.6%. OA between FISH and qRT-PCR was 90.8% with a k value of 0.81. Of interest, the disagreement between FISH and qRT-PCR was mostly restricted to equivocal cases. HER2 protein analysis suggested that qRT-PCR correlates better than FISH with HER2 protein levels, particularly where FISH fails to provide conclusive results.
Significance: qRT-PCR may outperform FISH in identifying patients overexpressing HER2 protein. Q-PCR cannot be used for HER2 status assessment, due to its suboptimal level of agreement with FISH. Both FISH and Q-PCR may be less accurate than qRT-PCR as surrogates of HER2 protein determination.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Detection of HER2 status in breast cancer: comparison of current methods with MLPA and real-time RT-PCR.Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2013;14(12):7621-8. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2013. PMID: 24460343
-
Quantitative RT-PCR assay of HER2 mRNA expression in formalin-fixed and paraffin-embedded breast cancer tissues.Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2014 Sep 15;7(10):6752-9. eCollection 2014. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2014. PMID: 25400755 Free PMC article.
-
Expression of HER2 and the coamplified genes GRB7 and MLN64 in human breast cancer: quantitative real-time reverse transcription-PCR as a diagnostic alternative to immunohistochemistry and fluorescence in situ hybridization.Clin Cancer Res. 2005 Dec 1;11(23):8348-57. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-05-0841. Clin Cancer Res. 2005. PMID: 16322295
-
A Comparison of IHC and FISH Cytogenetic Methods in the Evaluation of HER2 Status in Breast Cancer.Adv Clin Exp Med. 2015 Sep-Oct;24(5):899-903. doi: 10.17219/acem/27923. Adv Clin Exp Med. 2015. PMID: 26768643 Review.
-
Quantitative real-time PCR: a powerful ally in cancer research.Trends Mol Med. 2003 May;9(5):189-95. doi: 10.1016/s1471-4914(03)00047-9. Trends Mol Med. 2003. PMID: 12763523 Review.
Cited by
-
Neoadjuvant neratinib promotes ferroptosis and inhibits brain metastasis in a novel syngeneic model of spontaneous HER2+ve breast cancer metastasis.Breast Cancer Res. 2019 Aug 13;21(1):94. doi: 10.1186/s13058-019-1177-1. Breast Cancer Res. 2019. PMID: 31409375 Free PMC article.
-
How I treat HER2-low advanced breast cancer.Breast. 2023 Feb;67:116-123. doi: 10.1016/j.breast.2023.01.005. Epub 2023 Jan 12. Breast. 2023. PMID: 36669993 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Advances in research and current challenges in the treatment of advanced HER2-low breast cancer.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2025 Mar 19;13:1451471. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2025.1451471. eCollection 2025. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2025. PMID: 40177129 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Molecular Biological Determination of HER2 Status Using Both DNA and RNA Approaches: A Concordance Study with IHC Assessment.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Feb 27;26(5):2148. doi: 10.3390/ijms26052148. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40076767 Free PMC article.
-
Indocyanine Green Angiography to Predict Complications in Subcutaneous Mastectomy: A Single-Center Experience.J Pers Med. 2025 Jun 10;15(6):242. doi: 10.3390/jpm15060242. J Pers Med. 2025. PMID: 40559105 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Wolff AC, Hammond ME, Hicks DG, Dowsett M, McShane LM, Allison KH, Allred DC, Bartlett JM, Bilous M, Fitzgibbons P, Hanna W, Jenkins RB, Mangu PB, Paik S, Perez EA, Press MF, Spears PA, Vance GH, Viale G, Hayes DF, O. American Society of Clinical. P. College of American Recommendations for human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 testing in breast cancer: American Society of Clinical Oncology/College of American Pathologists clinical practice guideline update. J Clin Oncol. 2013;31:3997–4013. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2013.50.9984. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Press MF, Slamon DJ, Flom KJ, Park J, Zhou JY, Bernstein L. Evaluation of HER-2/neu gene amplification and overexpression: comparison of frequently used assay methods in a molecularly characterized cohort of breast cancer specimens. J Clin Oncol. 2002;20:3095–3105. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2002.09.094. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

