Pathophysiology of the cardio-renal syndromes types 1-5: An uptodate
- PMID: 28460776
- PMCID: PMC5415026
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ihj.2017.01.005
Pathophysiology of the cardio-renal syndromes types 1-5: An uptodate
Abstract
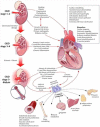
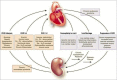
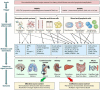
According to the recent definition proposed by the Consensus conference on Acute Dialysis Quality Initiative Group, the term cardio-renal syndrome (CRS) has been used to define different clinical conditions in which heart and kidney dysfunction overlap. Type 1 CRS (acute cardio- renal syndrome) is characterized by acute worsening of cardiac function leading to AKI (5, 6) in the setting of active cardiac disease such as ADHF, while type - 2 CRS occurs in a setting of chronic heart disease. Type 3 CRS is closely link to acute kidney injury (AKI), while type 4 represent cardiovascular involvement in chronic kidney disese (CKD) patients. Type 5 CRS represent cardiac and renal involvement in several diseases such as sepsis, hepato - renal syndrome and immune - mediated diseases.
Keywords: Acute kidney injury; Cardiorenal syndrome; Chronic kidney disease; Heart failure; Sepsis.
Copyright © 2017 Cardiological Society of India. Published by Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- Bargshaw S.M., Cruz D.M., Aspromonte N. Epidemiology of cardio –renal syndromes: workgroup statements from the 7th ADQI Consensus Conference. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2010;25:1406–1416. - PubMed
-
- Damman K., Navis G., Voors A.A. Worsening renal function and prognosis in heart failure: systematic review and meta-analysis. J Card Fail. 2007;13:599–608. - PubMed
-
- Ronco C. Cardiorenal syndromes: definition and classification. Contrib Nephrol. 2010;164:33–38. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

