Aqueous Angiography: Aqueous Humor Outflow Imaging in Live Human Subjects
- PMID: 28461013
- PMCID: PMC5522757
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ophtha.2017.03.058
Aqueous Angiography: Aqueous Humor Outflow Imaging in Live Human Subjects
Figures
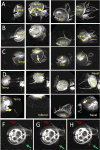
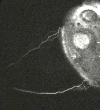
References
-
- Jacobs DS, Cox TA, Wagoner MD, et al. Capsule staining as an adjunct to cataract surgery: a report from the American Academy of Ophthalmology. Ophthalmology. 2006;113(4):707–13. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

