Structure of the Enterovirus 71 3C Protease in Complex with NK-1.8k and Indications for the Development of Antienterovirus Protease Inhibitor
- PMID: 28461310
- PMCID: PMC5487676
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.00298-17
Structure of the Enterovirus 71 3C Protease in Complex with NK-1.8k and Indications for the Development of Antienterovirus Protease Inhibitor
Abstract
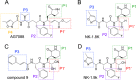
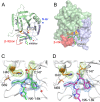
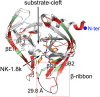
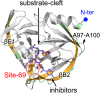
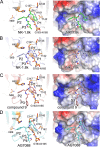
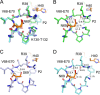
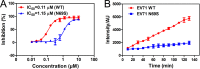
Hand-foot-and-mouth disease (HFMD), caused by enterovirus, is a threat to public health worldwide. To date, enterovirus 71 (EV71) has been one of the major causative agents of HFMD in the Pacific-Asia region, and outbreaks with EV71 cause millions of infections. However, no drug is currently available for clinical therapeutics. In our previous works, we developed a set of protease inhibitors (PIs) targeting the EV71 3C protease (3Cpro). Among these are NK-1.8k and NK-1.9k, which have various active groups and high potencies and selectivities. In the study described here, we determined the structures of the PI NK-1.8k in complex with wild-type (WT) and drug-resistant EV71 3Cpro Comparison of these structures with the structure of unliganded EV71 3Cpro and its complex with AG7088 indicated that the mutation of N69 to a serine residue destabilized the S2 pocket. Thus, the mutation influenced the cleavage activity of EV71 3Cpro and the inhibitory activity of NK-1.8k in an in vitro protease assay and highlighted that site 69 is an additional key site for PI design. More information for the optimization of the P1' to P4 groups of PIs was also obtained from these structures. Together with the results of our previous works, these in-depth results elucidate the inhibitory mechanism of PIs and shed light to develop PIs for the clinical treatment of infections caused by EV71 and other enteroviruses.
Keywords: EV71; crystal structure; inhibitor; mechanism; protease.
Copyright © 2017 American Society for Microbiology.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Enterovirus 71 and coxsackievirus A16 3C proteases: binding to rupintrivir and their substrates and anti-hand, foot, and mouth disease virus drug design.J Virol. 2011 Oct;85(19):10319-31. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00787-11. Epub 2011 Jul 27. J Virol. 2011. PMID: 21795339 Free PMC article.
-
Crystal structures of enterovirus 71 3C protease complexed with rupintrivir reveal the roles of catalytically important residues.J Virol. 2011 Oct;85(19):10021-30. doi: 10.1128/JVI.05107-11. Epub 2011 Aug 3. J Virol. 2011. PMID: 21813612 Free PMC article.
-
Structural basis for antiviral inhibition of the main protease, 3C, from human enterovirus 93.J Virol. 2011 Oct;85(20):10764-73. doi: 10.1128/JVI.05062-11. Epub 2011 Aug 10. J Virol. 2011. PMID: 21835784 Free PMC article.
-
The Function and Mechanism of Enterovirus 71 (EV71) 3C Protease.Curr Microbiol. 2020 Sep;77(9):1968-1975. doi: 10.1007/s00284-020-02082-4. Epub 2020 Jun 15. Curr Microbiol. 2020. PMID: 32556480 Review.
-
An update on enterovirus 71 infection and interferon type I response.Rev Med Virol. 2019 Jan;29(1):e2016. doi: 10.1002/rmv.2016. Epub 2018 Oct 30. Rev Med Virol. 2019. PMID: 30378208 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
4-Iminooxazolidin-2-One as a Bioisostere of Cyanohydrin Suppresses EV71 Proliferation by Targeting 3Cpro.Microbiol Spectr. 2021 Dec 22;9(3):e0102521. doi: 10.1128/Spectrum.01025-21. Epub 2021 Nov 17. Microbiol Spectr. 2021. PMID: 34787443 Free PMC article.
-
Hand, Foot, and Mouth Disease Challenges and Its Antiviral Therapeutics.Vaccines (Basel). 2023 Mar 1;11(3):571. doi: 10.3390/vaccines11030571. Vaccines (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36992155 Free PMC article.
-
Advances in anti-EV-A71 drug development research.J Adv Res. 2024 Feb;56:137-156. doi: 10.1016/j.jare.2023.03.007. Epub 2023 Mar 30. J Adv Res. 2024. PMID: 37001813 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Enterovirus A71 antivirals: Past, present, and future.Acta Pharm Sin B. 2022 Apr;12(4):1542-1566. doi: 10.1016/j.apsb.2021.08.017. Epub 2021 Aug 20. Acta Pharm Sin B. 2022. PMID: 35847514 Free PMC article.
-
Computational and experimental studies of salvianolic acid A targets 3C protease to inhibit enterovirus 71 infection.Front Pharmacol. 2023 Mar 2;14:1118584. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1118584. eCollection 2023. Front Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 36937869 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Chen C, Wang Y, Shan C, Sun Y, Xu P, Zhou H, Yang C, Shi PY, Rao Z, Zhang B, Lou Z. 2013. Crystal structure of enterovirus 71 RNA-dependent RNA polymerase complexed with its protein primer VPg: implication for a trans mechanism of VPg uridylylation. J Virol 87:5755–5768. doi:10.1128/JVI.02733-12. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

