Kinase Activities of RIPK1 and RIPK3 Can Direct IFN-β Synthesis Induced by Lipopolysaccharide
- PMID: 28461567
- PMCID: PMC5471631
- DOI: 10.4049/jimmunol.1601717
Kinase Activities of RIPK1 and RIPK3 Can Direct IFN-β Synthesis Induced by Lipopolysaccharide
Abstract
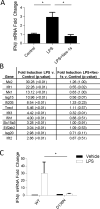
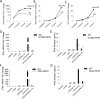
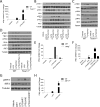
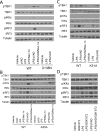
The innate immune response is a central element of the initial defense against bacterial and viral pathogens. Macrophages are key innate immune cells that upon encountering pathogen-associated molecular patterns respond by producing cytokines, including IFN-β. In this study, we identify a novel role for RIPK1 and RIPK3, a pair of homologous serine/threonine kinases previously implicated in the regulation of necroptosis and pathologic tissue injury, in directing IFN-β production in macrophages. Using genetic and pharmacologic tools, we show that catalytic activity of RIPK1 directs IFN-β synthesis induced by LPS in mice. Additionally, we report that RIPK1 kinase-dependent IFN-β production may be elicited in an analogous fashion using LPS in bone marrow-derived macrophages upon inhibition of caspases. Notably, this regulation requires kinase activities of both RIPK1 and RIPK3, but not the necroptosis effector protein, MLKL. Mechanistically, we provide evidence that necrosome-like RIPK1 and RIPK3 aggregates facilitate canonical TRIF-dependent IFN-β production downstream of the LPS receptor TLR4. Intriguingly, we also show that RIPK1 and RIPK3 kinase-dependent synthesis of IFN-β is markedly induced by avirulent strains of Gram-negative bacteria, Yersinia and Klebsiella, and less so by their wild-type counterparts. Overall, these observations identify unexpected roles for RIPK1 and RIPK3 kinases in the production of IFN-β during the host inflammatory responses to bacterial infection and suggest that the axis in which these kinases operate may represent a target for bacterial virulence factors.
Copyright © 2017 by The American Association of Immunologists, Inc.
Figures



References
-
- Christofferson DE, Li Y, Yuan J. Control of Life-or-Death Decisions by RIP1 Kinase. Annu Rev Physiol. 2014;76:129–50. - PubMed
-
- Kaczmarek A, Vandenabeele P, Krysko DV. Necroptosis: the release of damage-associated molecular patterns and its physiological relevance. Immunity. 2013;38:209–23. - PubMed
-
- Vanden Berghe T, Linkermann A, Jouan-Lanhouet S, Walczak H, Vandenabeele P. Regulated necrosis: the expanding network of non-apoptotic cell death pathways. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2014;15:135–47. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

