Cortical abnormalities in bipolar disorder: an MRI analysis of 6503 individuals from the ENIGMA Bipolar Disorder Working Group
- PMID: 28461699
- PMCID: PMC5668195
- DOI: 10.1038/mp.2017.73
Cortical abnormalities in bipolar disorder: an MRI analysis of 6503 individuals from the ENIGMA Bipolar Disorder Working Group
Abstract
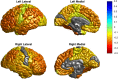
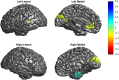
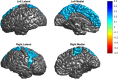
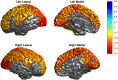
Despite decades of research, the pathophysiology of bipolar disorder (BD) is still not well understood. Structural brain differences have been associated with BD, but results from neuroimaging studies have been inconsistent. To address this, we performed the largest study to date of cortical gray matter thickness and surface area measures from brain magnetic resonance imaging scans of 6503 individuals including 1837 unrelated adults with BD and 2582 unrelated healthy controls for group differences while also examining the effects of commonly prescribed medications, age of illness onset, history of psychosis, mood state, age and sex differences on cortical regions. In BD, cortical gray matter was thinner in frontal, temporal and parietal regions of both brain hemispheres. BD had the strongest effects on left pars opercularis (Cohen's d=-0.293; P=1.71 × 10-21), left fusiform gyrus (d=-0.288; P=8.25 × 10-21) and left rostral middle frontal cortex (d=-0.276; P=2.99 × 10-19). Longer duration of illness (after accounting for age at the time of scanning) was associated with reduced cortical thickness in frontal, medial parietal and occipital regions. We found that several commonly prescribed medications, including lithium, antiepileptic and antipsychotic treatment showed significant associations with cortical thickness and surface area, even after accounting for patients who received multiple medications. We found evidence of reduced cortical surface area associated with a history of psychosis but no associations with mood state at the time of scanning. Our analysis revealed previously undetected associations and provides an extensive analysis of potential confounding variables in neuroimaging studies of BD.
Conflict of interest statement
AMM has received funding from Lilly, Janssen and Pfizer. It is unconnected with the current work. TvE has a contract with Otsuka Pharmaceutical Inc. The contract is not related to this work. UFM participated in the speaker’s bureau for Lundbeck Norway and was a consultant for Takeda Pharmaceuticals. ACB has received salaries from P1vital Ltd, which is unrelated to this work. PGR trained personnel for Janssen Pharmaceuticals. It is unconnected with the current work. DPH and WCD are employed by Janssen Research and Development, LLC. MB has received grant/research support from Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (DFG), Bundesministeriums für Bildung und Forschung (BMBF), American Foundation of Suicide Prevention. MB is/has been a consultant for AstraZeneca, Bristol Myers Squibb, Ferrer Internacional, Janssen, Lilly, Lundbeck, Merz, Neuraxpharm, Novartis, Otsuka, Servier, Takeda, and has received speaker honoraria from AstraZeneca, GlaxoSmithKline, Lilly, Lundbeck, Otsuka and Pfizer, which is all unrelated to this work. OAA has received speaker’s honorarium from Lundbeck, Otsuka and Lilly. The remaining authors declare no conflicts of interest. All authors have contributed to and approved the contents of this manuscript.
Figures
References
-
- Grande I, Berk M, Birmaher B, Vieta E. Bipolar disorder. Lancet 2016; 387: 1561–1572. - PubMed
-
- McGuffin P, Rijsdijk F, Andrew M, Sham P, Katz R, Cardno A. The heritability of bipolar affective disorder and the genetic relationship to unipolar depression. Arch Gen Psychiatry 2003; 60: 497–502. - PubMed
-
- Calabrese JR, Rapport DJ, Kimmel SE, Shelton MD. Controlled trials in bipolar I depression: focus on switch rates and efficacy. Eur Neuropsychopharmacol 1999; 9(Suppl 4): S109–S112. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- K23 MH074644/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- P41 EB015922/EB/NIBIB NIH HHS/United States
- K23 MH098130/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH095454/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH101111/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- MR/J008915/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- U54 EB020403/EB/NIBIB NIH HHS/United States
- 103703/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- 64410/CIHR/Canada
- 106469/CIHR/Canada
- R01 MH104284/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- K08 MH086786/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- 142255/CIHR/Canada
- P30 NS062691/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- K01 MH096077/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- K23 MH085096/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH075007/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- R01 MH107703/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH085667/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH090553/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH076971/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

