Gait analysis of patients with knee osteoarthritis highlights a pathological mechanical pathway and provides a basis for therapeutic interventions
- PMID: 28461915
- PMCID: PMC5367582
- DOI: 10.1302/2058-5241.1.000051
Gait analysis of patients with knee osteoarthritis highlights a pathological mechanical pathway and provides a basis for therapeutic interventions
Abstract
Knee osteoarthritis (OA) is a painful and incapacitating disease affecting a large portion of the elderly population, for which no cure exists. There is a critical need to enhance our understanding of OA pathogenesis, as a means to improve therapeutic options.Knee OA is a complex disease influenced by many factors, including the loading environment. Analysing knee biomechanics during walking - the primary cyclic load-bearing activity - is therefore particularly relevant.There is evidence of meaningful differences in the knee adduction moment, flexion moment and flexion angle during walking between non-OA individuals and patients with medial knee OA. Furthermore, these kinetic and kinematic gait variables have been associated with OA progression.Gait analysis provides the critical information needed to understand the role of ambulatory biomechanics in OA development, and to design therapeutic interventions. Multidisciplinary research is necessary to relate the biomechanical alterations to the structural and biological components of OA. Cite this article: Favre J, Jolles BM. Analysis of gait, knee biomechanics and the physiopathology of knee osteoarthritis in the development of therapeutic interventions. EFORT Open Rev 2016;1:368-374. DOI: 10.1302/2058-5241.1.000051.
Keywords: adduction moment; ambulatory mechanics; flexion angle; flexion moment; gait analysis; knee; osteoarthritis.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interest: No interests declared.
Figures
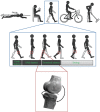
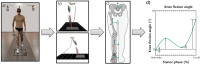
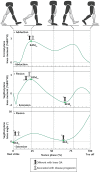
References
-
- Helmick CG, Felson DT, Lawrence RC, et al. ; National Arthritis Data Workgroup. Estimates of the prevalence of arthritis and other rheumatic conditions in the United States. Part I. Arthritis Rheum 2008;58:15-25. - PubMed
-
- Andriacchi TP, Favre J. The nature of in vivo mechanical signals that influence cartilage health and progression to knee osteoarthritis. Curr Rheumatol Rep 2014;16:463. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

