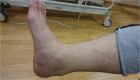
Non-insertional Achilles tendinopathy
- PMID: 28461917
- PMCID: PMC5367540
- DOI: 10.1302/2058-5241.1.160024
Non-insertional Achilles tendinopathy
Abstract
Non-insertional Achilles tendinopathy is a degenerative condition characterised by pain on activity.Eccentric stretching is the most effective treatment.Surgical treatment is reserved for recalcitrant cases.Minimally-invasive and tendinoscopic treatments are showing promising results. Cite this article: Pearce CJ, Tan A. Non-insertional Achilles tendinopathy. EFORT Open Rev 2016;1:383-390. DOI: 10.1302/2058-5241.1.160024.
Keywords: Achilles tendinopathy; clincal presentation; non-insertional,aetiology; non-operative treatment; operative treatment.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interest: CJP is a member of the editorial board of the journal Knee Surgery, Sports Traumatology, Arthroscopy, and has been a paid speaker for Smith & Nephew and DePuy Synthes. The above declarations have no connection or commercial link to this paper.
Figures


References
-
- Puddu G, Ippolito E, Postacchini F. A classification of Achilles tendon disease. Am J Sports Med 1976;4:145-150. - PubMed
-
- Alfredson H, Ohberg L, Forsgren S. Is vasculo-neural ingrowth the cause of pain in chronic Achilles tendinosis? An investigation using ultrasonography and colour Doppler, immunohistochemistry, and diagnostic injections. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 2003;11:334-338. - PubMed
-
- Khan KM, Cook JL, Bonar F, Harcourt P, Astrom M. Histopathology of common tendinopathies. Update and implications for clinical management. Sports Med 1999;27:393-408. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

