Distal radioulnar joint arthroplasty with implants: a systematic review
- PMID: 28461947
- PMCID: PMC5367606
- DOI: 10.1302/2058-5241.1.160008
Distal radioulnar joint arthroplasty with implants: a systematic review
Abstract
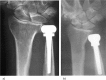
A severely painful, dysfunctional, or destroyed distal radio-ulnar joint (DRUJ) can be reconstructed by fusion, interposition of soft tissue, or by arthroplasty using prostheses.The objective of this study was to review the literature on implants and evaluate their effectiveness in terms of pain relief, range of motion and longevity.A search was carried out using protocols and well-defined criteria in PubMed, the Cochrane Library and by screening reference lists. The review was conducted according to PRISMA guidelines.Of the 27 publications reporting on nine different implants, we excluded reports with less than five cases and silastic replacements of the ulna head. Eighteen publications describing a total of five implants were selected for analysis. Nine of the publications were useful for the evaluation of implant longevity. Despite methodological shortcomings in many of the source documents, a summary estimate was possible.It seems that DRUJ implants have good potential to improve function through pain reduction; an improvement was observed in 17 series, although it was significant in only seven series.Instability is not uncommon with ulna head-only implants, but they cause fewer clinical problems and re-interventions than might be expected.The risk of deep infection is small with the available implants.Overall implant survival in papers with at least five years' follow-up is 95%, with a slightly better longevity of 98% for the constrained implants.Periprosthetic osteolysis/radiolucency is frequently reported. Its causes and consequences are not clarified. Cite this article: Calcagni M, Giesen T. Distal radioulnar joint arthroplasty with implants: a systematic review. EFORT Open Rev 2016;1:191-196. DOI: 10.1302/2058-5241.1.160008.
Keywords: arthroplasty; distal radioulnar joint; implants.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interest: Dr. Calcagni declares fees outside of the submitted work as a speaker for Swedish Orphan Biovitrum.
Figures



References
-
- Hagert CG. The distal radioulnar joint in relation to the whole forearm. Clin Orthop Relat Res 1992;275:56-64. PMID:1735234. - PubMed
-
- Lees VC, Scheker LR. The radiological demonstration of dynamic ulnar impingement. J Hand Surg [Br] 1997;22:448-50.
-
- Schuurman AH, Teunis T. A new total distal radioulnar joint prosthesis: functional outcome. J Hand Surg [Am] 2010;35:1614-19. PMID:20843612. - PubMed
-
- van Schoonhoven J, Herbert TH, Krimmer H. Neue Konzepte der Endoprothetik des distalen Radioulnargelenkes [New concepts for endoprostheses of the distal radio-ulnar joint]. Handchir Mikrochir Plast Chir 1998;30:387-392. PMID:9888011. [in German]. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

