Distal triceps ruptures
- PMID: 28461956
- PMCID: PMC5367525
- DOI: 10.1302/2058-5241.1.000038
Distal triceps ruptures
Abstract
Distal triceps ruptures are rare injuries due to the special anatomical features of the muscle and tendon-bone junction.This injury typically occurs at the tendon-bone junction due to an eccentric contraction of the muscle.The treatment is controversial, especially in partial ruptures; surgical repair is indicated for complete ruptures of the distal triceps tendon.Several repair techniques have been described for acute complete ruptures.Chronic ruptures often require reconstruction rather than direct repair. Cite this article: Demirhan M, Ersen A. Distal triceps ruptures. EFORT Open Rev 2016;1:255-259. DOI: 10.1302/2058-5241.1.000038.
Keywords: aetiology; anatomy; diagnosis; distal rupture; transosseous repair; treatment; triceps.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interest: None declared.
Figures


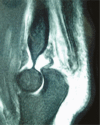


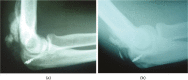
References
-
- Anzel SH, Covey KW, Weiner AD, Lipscomb PR. Disruption of muscles and tendons; an analysis of 1,014 cases. Surgery 1959;45:406-14. - PubMed
-
- Tom JA, Kumar NS, Cerynik DL, Mashru R, Parrella MS. Diagnosis and treatment of triceps tendon injuries: a review of the literature. Clin J Sport Med 2014;24:197-204. - PubMed
-
- Yeh PC, Dodds SD, Smart LR, Mazzocca AD, Sethi PM. Distal triceps rupture. J Am Acad Orthop Surg 2010;18:31-40. - PubMed
-
- Keener JD, Chafik D, Kim HM, Galatz LM, Yamaguchi K. Insertional anatomy of the triceps brachii tendon. J Shoulder Elbow Surg 2010;19:399-405. - PubMed
-
- Mair SD, Isbell WM, Gill TJ, Schlegel TF, Hawkins RJ. Triceps tendon ruptures in professional football players. Am J Sports Med 2004;32:431-4. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

