Dual Active Site in the Endolytic Transglycosylase gp144 of Bacteriophage phiKZ
- PMID: 28461978
- PMCID: PMC5406664
Dual Active Site in the Endolytic Transglycosylase gp144 of Bacteriophage phiKZ
Abstract
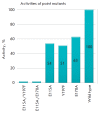
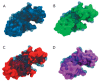
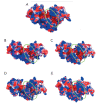
Lytic transglycosylases are abundant peptidoglycan lysing enzymes that degrade the heteropolymers of bacterial cell walls in metabolic processes or in the course of a bacteriophage infection. The conventional catalytic mechanism of transglycosylases involves only the Glu or Asp residue. Endolysin gp144 of Pseudomonas aeruginosa bacteriophage phiKZ belongs to the family of Gram-negative transglycosylases with a modular composition and C-terminal location of the catalytic domain. Glu115 of gp144 performs the predicted role of a catalytic residue. However, replacement of this residue does not completely eliminate the activity of the mutant protein. Site-directed mutagenesis has revealed the participation of Tyr197 in the catalytic mechanism, as well as the presence of a second active site involving Glu178 and Tyr147. The existence of the dual active site was supported by computer modeling and monitoring of the molecular dynamics of the changes in the conformation and surface charge distribution as a consequence of point mutations.
Keywords: bacteriophage phiKZ; endolysin; enzyme active site; molecular dynamics; site-directed mutagenesis; transglycosylase.
Figures



References
-
- Krylov V.N., Dela Cruz D.M., Hertveldt K., Ackermann H.W.. Arch. Virol. 2007;152(10):1955–1959. - PubMed
-
- Krylov V.N., Miroshnikov K.A., Krylov S.V., Veiko V.P., Pletneva E.A., Shaburova O.V., Burkal’tseva M.V.. Genetika. 2010;46(2):159–167. - PubMed
-
- Fokine A., Battisti A.J., Bowman V.D., Efimov A.V., Kurochkina L.P., Chipman P.R., Mesyanzhinov V.V., Rossmann M.G.. Structure. 2007;15(9):1099–1104. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
