Caspase-8: regulating life and death
- PMID: 28462525
- PMCID: PMC5417704
- DOI: 10.1111/imr.12541
Caspase-8: regulating life and death
Abstract
Roles for cell death in development, homeostasis, and the control of infections and cancer have long been recognized. Although excessive cell damage results in passive necrosis, cells can be triggered to engage molecular programs that result in cell death. Such triggers include cellular stress, oncogenic signals that engage tumor suppressor mechanisms, pathogen insults, and immune mechanisms. The best-known forms of programmed cell death are apoptosis and a recently recognized regulated necrosis termed necroptosis. Of the two best understood pathways of apoptosis, the extrinsic and intrinsic (mitochondrial) pathways, the former is induced by the ligation of death receptors, a subset of the TNF receptor (TNFR) superfamily. Ligation of these death receptors can also induce necroptosis. The extrinsic apoptosis and necroptosis pathways regulate each other and their balance determines whether cells live. Integral in the regulation and initiation of death receptor-mediated activation of programmed cell death is the aspartate-specific cysteine protease (caspase)-8. This review describes the role of caspase-8 in the initiation of extrinsic apoptosis execution and the mechanism by which caspase-8 inhibits necroptosis. The importance of caspase-8 in the development and homeostasis and the way that dysfunctional caspase-8 may contribute to the development of malignancies in mice and humans are also explored.
Keywords: apoptosis; caspase-8; development; hematopoiesis; inflammation; necroptosis.
© 2017 John Wiley & Sons A/S. Published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors do not declare any conflict of interest.
Figures
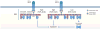
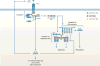


References
-
- Hanahan D, Weinberg RA. The hallmarks of cancer. Cell. 2000;100:57–70. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

