Transcriptome analysis illuminates the nature of the intracellular interaction in a vertebrate-algal symbiosis
- PMID: 28462779
- PMCID: PMC5413350
- DOI: 10.7554/eLife.22054
Transcriptome analysis illuminates the nature of the intracellular interaction in a vertebrate-algal symbiosis
Abstract
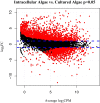
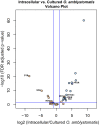
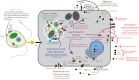
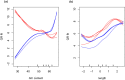
During embryonic development, cells of the green alga Oophila amblystomatis enter cells of the salamander Ambystoma maculatum forming an endosymbiosis. Here, using de novo dual-RNA seq, we compared the host salamander cells that harbored intracellular algae to those without algae and the algae inside the animal cells to those in the egg capsule. This two-by-two-way analysis revealed that intracellular algae exhibit hallmarks of cellular stress and undergo a striking metabolic shift from oxidative metabolism to fermentation. Culturing experiments with the alga showed that host glutamine may be utilized by the algal endosymbiont as a primary nitrogen source. Transcriptional changes in salamander cells suggest an innate immune response to the alga, with potential attenuation of NF-κB, and metabolic alterations indicative of modulation of insulin sensitivity. In stark contrast to its algal endosymbiont, the salamander cells did not exhibit major stress responses, suggesting that the host cell experience is neutral or beneficial.
Keywords: Ambystoma maculatum; Oophila amblystomatis; RNA-seq; ecology; evolutionary biology; genomics; symbiosis; transcriptomics.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that no competing interests exist.
Figures






Comment in
-
Gasping for air.Elife. 2017 May 2;6:e27004. doi: 10.7554/eLife.27004. Elife. 2017. PMID: 28462778 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bachmann MD, Carlton RG, Burkholder JM, Wetzel RG. Symbiosis between salamander eggs and green algae: microelectrode measurements inside eggs demonstrate effect of photosynthesis on oxygen concentration. Canadian Journal of Zoology. 1986;64:1586–1588. doi: 10.1139/z86-239. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

