Sphingolipids and Lipoproteins in Health and Metabolic Disorders
- PMID: 28462811
- PMCID: PMC5474131
- DOI: 10.1016/j.tem.2017.03.005
Sphingolipids and Lipoproteins in Health and Metabolic Disorders
Abstract
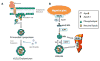
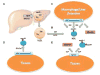
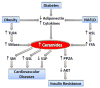
Sphingolipids are structurally and functionally diverse molecules with significant physiologic functions and are found associated with cellular membranes and plasma lipoproteins. The cellular and plasma concentrations of sphingolipids are altered in several metabolic disorders and may serve as prognostic and diagnostic markers. Here we discuss various sphingolipid transport mechanisms and highlight how changes in cellular and plasma sphingolipid levels contribute to cardiovascular disease, obesity, diabetes, insulin resistance, and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD). Understanding of the mechanisms involved in intracellular transport, secretion, and extracellular transport may provide novel information that might be amenable to therapeutic targeting for the treatment of various metabolic disorders.
Keywords: MTP; ceramide; lipoproteins; metabolic disorders; sphingolipids; sphingomyelin.
Copyright © 2017 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest with the contents of this article.
Figures

References
-
- Feingold KR, Grunfeld C. Introduction to Lipids and Lipoproteins. In: De Groot LJ, Chrousos G, Dungan K, et al., editors. Endotext [Internet] South Dartmouth (MA): MDText.com, Inc; 2000. Updated 2015 Jun 10. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK305896/
-
- Walsh MT, Hussain MM. Targeting microsomal triglyceride transfer protein and lipoprotein assembly to treat homozygous familial hypercholesterolemia. Crit Rev Clin Lab Sci. 2016:1–23. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

