Asymmetrical barcode adapter-assisted recovery of duplicate reads and error correction strategy to detect rare mutations in circulating tumor DNA
- PMID: 28462938
- PMCID: PMC5411960
- DOI: 10.1038/srep46678
Asymmetrical barcode adapter-assisted recovery of duplicate reads and error correction strategy to detect rare mutations in circulating tumor DNA
Abstract
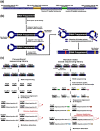
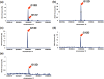
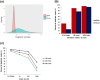
Deep sequencing is required for the highly sensitive detection of rare variants in circulating tumor DNA (ctDNA). However, there remains a challenge for improved sensitivity and specificity. Maximum-depth sequencing is crucial to detect minority mutations that contribute to cancer progression. The associated costs become prohibitive as the numbers of targets and samples increase. We describe the targeted sequencing of KRAS in plasma samples using an efficient barcoding approach to recover discarded reads marked as duplicates. Combined with an error-removal strategy, we anticipate that our method could improve the accuracy of genotype calling, especially to detect rare mutations in the monitoring of ctDNA.
Conflict of interest statement
J.A., B.H., H.K., and D.B. are authors of a patent application for the method described in this paper (Next-generation sequencing data analysis using barcoded asymmetric sequencing adapter, 10-2015-0077246, 10-2016-0068355, PCT/KR2016/005817). The remaining authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
TNER: a novel background error suppression method for mutation detection in circulating tumor DNA.BMC Bioinformatics. 2018 Oct 20;19(1):387. doi: 10.1186/s12859-018-2428-3. BMC Bioinformatics. 2018. PMID: 30342468 Free PMC article.
-
Detection of Rare Mutations in CtDNA Using Next Generation Sequencing.J Vis Exp. 2017 Aug 24;(126):56342. doi: 10.3791/56342. J Vis Exp. 2017. PMID: 28872127 Free PMC article.
-
Ultrasensitive Detection of Circulating Tumor DNA in Lymphoma via Targeted Hybridization Capture and Deep Sequencing of Barcoded Libraries.Methods Mol Biol. 2019;1956:383-435. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-9151-8_20. Methods Mol Biol. 2019. PMID: 30779047
-
Technical progress in circulating tumor DNA analysis using next generation sequencing.Mol Cell Probes. 2020 Feb;49:101480. doi: 10.1016/j.mcp.2019.101480. Epub 2019 Nov 8. Mol Cell Probes. 2020. PMID: 31711827 Review.
-
Potential clinical utility of ultrasensitive circulating tumor DNA detection with CAPP-Seq.Expert Rev Mol Diagn. 2015 Jun;15(6):715-9. doi: 10.1586/14737159.2015.1019476. Epub 2015 Mar 16. Expert Rev Mol Diagn. 2015. PMID: 25773944 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Barcode-free next-generation sequencing error validation for ultra-rare variant detection.Nat Commun. 2019 Feb 28;10(1):977. doi: 10.1038/s41467-019-08941-4. Nat Commun. 2019. PMID: 30816127 Free PMC article.
-
Detecting Rare Mutations and DNA Damage with Sequencing-Based Methods.Trends Biotechnol. 2018 Jul;36(7):729-740. doi: 10.1016/j.tibtech.2018.02.009. Epub 2018 Mar 14. Trends Biotechnol. 2018. PMID: 29550161 Free PMC article. Review.
-
MRD in AML: The Role of New Techniques.Front Oncol. 2019 Jul 23;9:655. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2019.00655. eCollection 2019. Front Oncol. 2019. PMID: 31396481 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

