Duration of Androgen Deprivation in Locally Advanced Prostate Cancer: Long-Term Update of NRG Oncology RTOG 9202
- PMID: 28463149
- PMCID: PMC5603177
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2017.02.004
Duration of Androgen Deprivation in Locally Advanced Prostate Cancer: Long-Term Update of NRG Oncology RTOG 9202
Abstract
Purpose: Trial RTOG 9202 was a phase 3 randomized trial designed to determine the optimal duration of androgen deprivation therapy (ADT) when combined with definitive radiation therapy (RT) in the treatment of locally advanced nonmetastatic adenocarcinoma of the prostate. Long-term follow-up results of this study now available are relevant to the management of this disease.
Methods and materials: Men (N=1554) with adenocarcinoma of the prostate (cT2c-T4, N0-Nx) with a prostate-specific antigen (PSA) <150 ng/mL and no evidence of distant metastasis were randomized (June 1992 to April 1995) to short-term ADT (STAD: 4 months of flutamide 250 mg 3 times per day and goserelin 3.6 mg per month) and definitive RT versus long-term ADT (LTAD: STAD with definitive RT plus an additional 24 months of monthly goserelin).
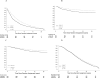
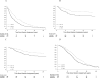
Results: Among 1520 protocol-eligible and evaluable patients, the median follow-up time for this analysis was 19.6 years. In analysis adjusted for prognostic covariates, LTAD improved disease-free survival (29% relative reduction in failure rate, P<.0001), local progression (46% relative reduction, P=.02), distant metastases (36% relative reduction, P<.0001), disease-specific survival (30% relative reduction, P=.003), and overall survival (12% relative reduction, P=.03). Other-cause mortality (non-prostate cancer) did not differ (5% relative reduction, P=.48).
Conclusions: LTAD and RT is superior to STAD and RT for the treatment of locally advanced nonmetastatic adenocarcinoma of the prostate and should be considered the standard of care.
Published by Elsevier Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
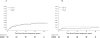
Comment in
-
The Long and Short of It: New Lessons on the Optimal Duration of Androgen Deprivation Therapy for High-Risk Prostate Cancer and Where We Need to Go From Here.Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2018 Aug 1;101(5):1014-1017. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2018.01.063. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2018. PMID: 30047408 No abstract available.
References
-
-
****
-
-
- Pilepich MV, Winter K, John MJ, et al. Phase III radiation therapy oncology group (RTOG) trial 8610 of androgen deprivation adjuvant to definitive radiotherapy in locally advanced carcinoma of the prostate. Int J Rad Onc Biol & Phys. 2001;50:1243–1252. - PubMed
-
- Bolla M, Collette L, Blank L, et al. Long term results with immediate androgen suppression and external irradiation in patients with locally advanced prostate cancer (an EORTC study): A phase III randomized trial. Lancet. 2002;360:103–106. - PubMed
-
- Bolla M, de Reijke T, Van Tienhoven G, et al. Duration of androgen suppression in the treatment of prostate cancer. New Eng Jour of Med. 2009;360(24):2516–2027. - PubMed
-
-
****
-
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

