Sensitivity of spatially offset Raman spectroscopy (SORS) to subcortical bone tissue
- PMID: 28464501
- PMCID: PMC5971662
- DOI: 10.1002/jbio.201600317
Sensitivity of spatially offset Raman spectroscopy (SORS) to subcortical bone tissue
Abstract
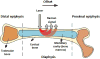
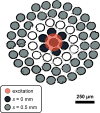
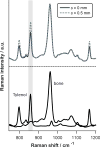
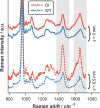
The development of spatially offset Raman spectroscopy (SORS) has enabled deep, non-invasive chemical characterization of turbid media. Here, we use SORS to measure subcortical bone tissue and depth-resolved biochemical variability in intact, exposed murine bones. We also apply the technique to study a mouse model of the genetic bone disorder osteogenesis imperfecta. The results suggest that SORS is more sensitive to disease-related biochemical differences in subcortical trabecular bone and marrow than conventional Raman measurements.
Keywords: bone; osteogenesis imperfecta; spatially offset Raman spectroscopy.
© 2017 Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, Weinheim.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

