Highly sensitive and accurate detection of C-reactive protein by CdSe/ZnS quantum dot-based fluorescence-linked immunosorbent assay
- PMID: 28464873
- PMCID: PMC5414212
- DOI: 10.1186/s12951-017-0267-4
Highly sensitive and accurate detection of C-reactive protein by CdSe/ZnS quantum dot-based fluorescence-linked immunosorbent assay
Abstract
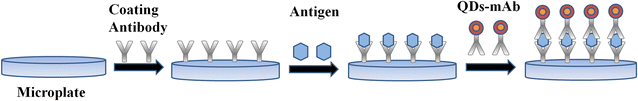
Background: The conventional and widely used enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays (ELISA), due to specificity and high-sensitivity, were suitable in vitro diagnosis. But enzymes are vulnerable to the external conditions, and the complex operation steps limit its application. Semiconductor quantum dots have been successfully used in biological and medical research due to the high photoluminescence and high resistance to photobleaching. In this study, we have developed a novel quantum dot-labeled immunosorbent assay for rapid disease detection of C-reactive protein (CRP).
Results: The assay for the detection of CRP can provide a wide analytical range of 1.56-400 ng/mL with the limit of detection (LOD) = 0.46 ng/mL and the limit of quantification = 1.53 ng/mL. The precision of the assay has been confirmed for low coefficient of variation, less than 10% (intra-assay) and less than 15% (inter-assay). The accuracy of assay meets the requirements with the recoveries of 95.4-105.7%. Furthermore, clinical samples have been collected and used for correlation analysis between this FLISA and gold standard Roche immunoturbidimetry. It shows excellent accurate concordance and the correlation coefficient value (R) is as high as 0.989 (n = 34).
Conclusions: This in vitro quantum dot-based detection method offers a lower LOD and a wide liner detection range than ELISA. The total reaction time is only 50 min, which is much shorter than the commercialization ELISA (about 120 min). All of the results show that a convenient, sensitive, and accurate fluorescence-linked immunosorbent assay method has been well established for the detection of CRP samples. Therefore, this method has immense potential for the development of rapid and cost-effective in vitro diagnostic kits.
Keywords: C-reactive protein; Fluorescence-linked immunosorbent assay; Fluorescent probe; Quantum dots.
Figures






Similar articles
-
Magnetic immunoassay using CdSe/ZnS quantum dots as fluorescent probes to detect the level of DNA methyltransferase 1 in human serum sample.Int J Nanomedicine. 2018 Jan 17;13:429-437. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S152618. eCollection 2018. Int J Nanomedicine. 2018. PMID: 29403274 Free PMC article.
-
A Novel Fluoroimmunoassay for Detecting Ruscogenin with Monoclonal Antibodies Conjugated with CdSe/ZnS Quantum Dots.Molecules. 2017 Jul 26;22(8):1250. doi: 10.3390/molecules22081250. Molecules. 2017. PMID: 28933731 Free PMC article.
-
Detection of ochratoxin A by quantum dots-based fluorescent immunochromatographic assay.Anal Bioanal Chem. 2021 Jan;413(1):183-192. doi: 10.1007/s00216-020-02990-1. Epub 2020 Oct 16. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2021. PMID: 33064163
-
Stability and fluorescence quantum yield of CdSe-ZnS quantum dots--influence of the thickness of the ZnS shell.Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2008;1130:235-41. doi: 10.1196/annals.1430.021. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2008. PMID: 18596353 Review.
-
Recent advances in quantum dot-based fluorescence-linked immunosorbent assays.Nanoscale. 2023 Mar 23;15(12):5560-5578. doi: 10.1039/d2nr07247e. Nanoscale. 2023. PMID: 36866747 Review.
Cited by
-
Detection and discrimination of sulfur dioxide using a colorimetric sensor array.RSC Adv. 2022 Sep 13;12(40):25852-25859. doi: 10.1039/d2ra04251g. eCollection 2022 Sep 12. RSC Adv. 2022. PMID: 36199613 Free PMC article.
-
Eu-Chelate Polystyrene Microsphere-Based Lateral Flow Immunoassay Platform for hs-CRP Detection.Biosensors (Basel). 2022 Nov 7;12(11):977. doi: 10.3390/bios12110977. Biosensors (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36354486 Free PMC article.
-
Fluorometric lateral flow immunochromatographic zearalenone assay by exploiting a quencher system composed of carbon dots and silver nanoparticles.Mikrochim Acta. 2018 Jul 25;185(8):388. doi: 10.1007/s00604-018-2916-1. Mikrochim Acta. 2018. PMID: 30046913
-
Optical Sensors Based on II-VI Quantum Dots.Nanomaterials (Basel). 2019 Feb 2;9(2):192. doi: 10.3390/nano9020192. Nanomaterials (Basel). 2019. PMID: 30717393 Free PMC article. Review.
-
VEGF Detection via Simplified FLISA Using a 3D Microfluidic Disk Platform.Biosensors (Basel). 2021 Aug 11;11(8):270. doi: 10.3390/bios11080270. Biosensors (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34436072 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Rifai N, Tracy RP, Ridker PM. Clinical efficacy of an automated high-sensitivity C-reactive protein assay. Clin Chem. 1999;45:2136–2141. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

