The role of apoptosis repressor with a CARD domain (ARC) in the therapeutic resistance of renal cell carcinoma (RCC): the crucial role of ARC in the inhibition of extrinsic and intrinsic apoptotic signalling
- PMID: 28464919
- PMCID: PMC5414156
- DOI: 10.1186/s12964-017-0170-5
The role of apoptosis repressor with a CARD domain (ARC) in the therapeutic resistance of renal cell carcinoma (RCC): the crucial role of ARC in the inhibition of extrinsic and intrinsic apoptotic signalling
Abstract
Background: Renal cell carcinomas (RCCs) display broad resistance against conventional radio- and chemotherapies, which is due at least in part to impairments in both extrinsic and intrinsic apoptotic pathways. One important anti-apoptotic factor that is strongly overexpressed in RCCs and known to inhibit both apoptotic pathways is ARC (apoptosis repressor with a CARD domain).
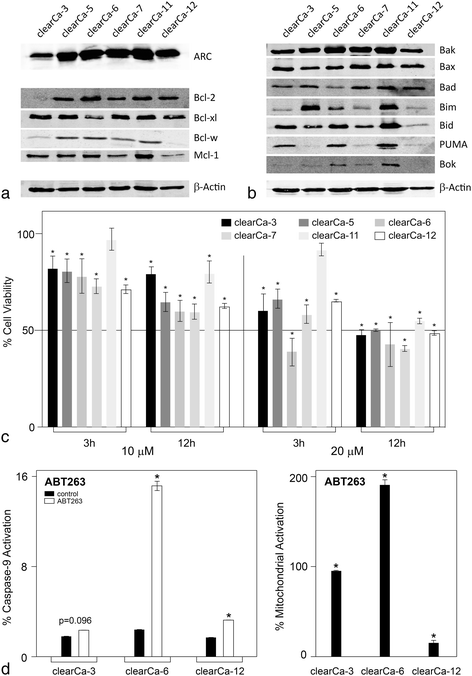
Methods: Expression and subcellular distribution of ARC in RCC tissue samples and RCC cell lines were determined by immunohistochemistry and fluorescent immunohistochemistry, respectively. Extrinsic and intrinsic apoptosis signalling were induced by TRAIL (TNF-related apoptosis-inducing ligand), ABT-263 or topotecan. ARC knock-down was performed in clearCa-12 cells using lentiviral transduction of pGIPZ. shRNAmir constructs. Extrinsic respectively intrinsic apoptosis were induced by TRAIL (TNF-related apoptosis-inducing ligand), ABT263 or topotecan. Potential synergistic effects were tested by pre-treatment with topotecan and subsequent treatment with ABT263. Activation of different caspases and mitochondrial depolarisation (JC-1 staining) were analysed by flow cytometry. Protein expression of Bcl-2 family members and ARC in RCC cell lines was measured by Western blotting. Statistical analysis was performed by Student's t-test.
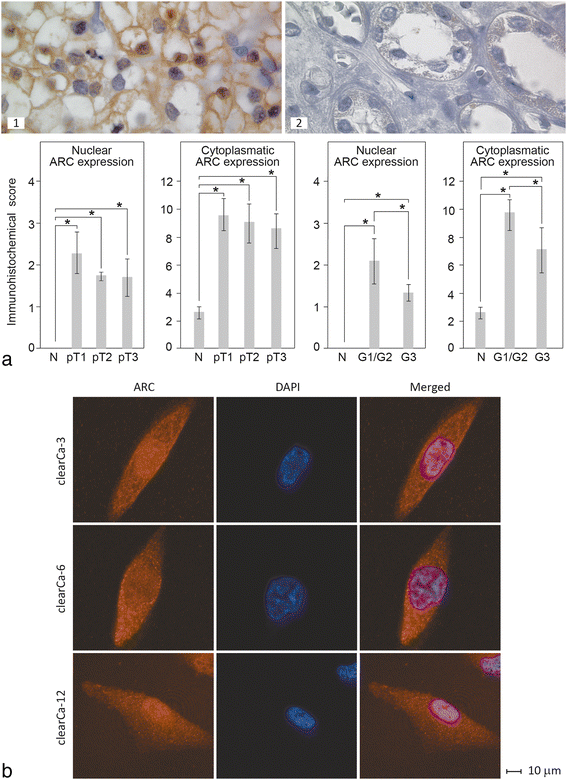
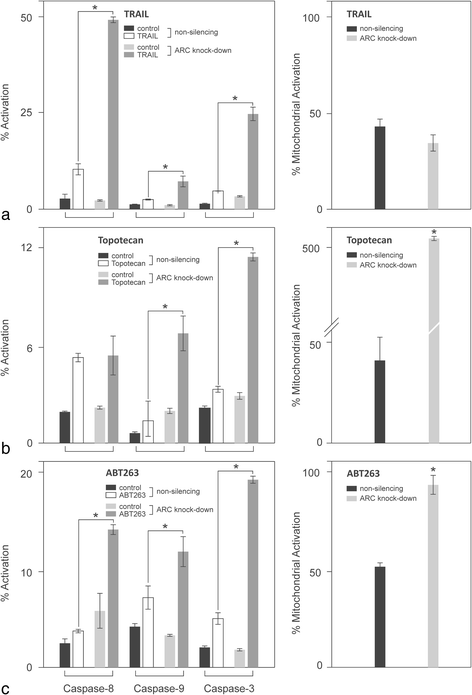
Results: Regarding the extrinsic pathway, ARC knockdown strongly enhanced TRAIL-induced apoptosis by increasing the activation level of caspase-8. Regarding the intrinsic pathway, ARC, which was only weakly expressed in the nuclei of RCCs in vivo, exerted its anti-apoptotic effect by impairing mitochondrial activation rather than inhibiting p53. Topotecan- and ABT-263-induced apoptosis was strongly enhanced following ARC knockdown in RCC cell lines. In addition, topotecan pre-treatment enhanced ABT-263-induced apoptosis and this effect was amplified in ARC-knockdown cells.
Conclusion: Taken together, our results are the first to demonstrate the importance of ARC protein in the inhibition of both the extrinsic and intrinsic pathways of apoptosis in RCCs. In this context, ARC cooperates with anti-apoptotic Bcl-2 family members to exert its strong anti-apoptotic effects and is therefore an important factor not only in the therapeutic resistance but also in future therapy strategies (i.e., Bcl-2 inhibitors) in RCC. In sum, targeting of ARC may enhance the therapeutic response in combination therapy protocols.
Keywords: ABT-263; ARC; Apoptosis; Bcl-2 family; TRAIL; renal cell carcinoma (RCC).
Figures



Similar articles
-
Sensitivity to TRAIL/APO-2L-mediated apoptosis in human renal cell carcinomas and its enhancement by topotecan.Cell Death Differ. 2000 Nov;7(11):1127-36. doi: 10.1038/sj.cdd.4400746. Cell Death Differ. 2000. PMID: 11139287
-
ABT-263 sensitizes TRAIL-resistant hepatocarcinoma cells by downregulating the Bcl-2 family of anti-apoptotic protein.Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2012 Mar;69(3):799-805. doi: 10.1007/s00280-011-1763-0. Epub 2011 Oct 29. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2012. PMID: 22037880
-
Frequent loss of expression of the pro-apoptotic protein Bim in renal cell carcinoma: evidence for contribution to apoptosis resistance.Oncogene. 2007 Oct 25;26(49):7038-48. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1210510. Epub 2007 May 7. Oncogene. 2007. PMID: 17486061
-
Apoptosis signaling and BCL-2 pathways provide opportunities for novel targeted therapeutic strategies in hematologic malignances.Blood Rev. 2018 Jan;32(1):8-28. doi: 10.1016/j.blre.2017.08.004. Epub 2017 Aug 8. Blood Rev. 2018. PMID: 28802908 Review.
-
Inhibiting the inhibitors: Targeting anti-apoptotic proteins in cancer and therapy resistance.Drug Resist Updat. 2020 Sep;52:100712. doi: 10.1016/j.drup.2020.100712. Epub 2020 Jun 20. Drug Resist Updat. 2020. PMID: 32599435 Review.
Cited by
-
Expression of apoptosis repressor with caspase recruitment domain (ARC) in familial adenomatous polyposis (FAP) adenomas and its correlation with DNA mismatch repair proteins, p53, Bcl-2, COX-2 and beta-catenin.Cell Commun Signal. 2021 Feb 12;19(1):15. doi: 10.1186/s12964-020-00702-x. Cell Commun Signal. 2021. PMID: 33579312 Free PMC article.
-
Role of apoptosis repressor with caspase recruitment domain (ARC) in cancer.Oncol Lett. 2019 Dec;18(6):5691-5698. doi: 10.3892/ol.2019.10981. Epub 2019 Oct 11. Oncol Lett. 2019. PMID: 31788041 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Identification of FDFT1 as a potential biomarker associated with ferroptosis in ccRCC.Cancer Med. 2022 Nov;11(21):3993-4004. doi: 10.1002/cam4.4716. Epub 2022 Mar 24. Cancer Med. 2022. PMID: 35322581 Free PMC article.
-
Osalmid sensitizes clear cell renal cell carcinoma to navitoclax through a STAT3/BCL-XL pathway.Cancer Lett. 2025 Mar 31;613:217514. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2025.217514. Epub 2025 Jan 31. Cancer Lett. 2025. PMID: 39894195 Free PMC article.
-
SNU-333 Cells as an Appropriate Cell Line for the Orthotopic Renal Cell Carcinoma Model.Technol Cancer Res Treat. 2021 Jan-Dec;20:15330338211038487. doi: 10.1177/15330338211038487. Technol Cancer Res Treat. 2021. PMID: 34490820 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

