Energy sensing pathways: Bridging type 2 diabetes and colorectal cancer?
- PMID: 28465145
- PMCID: PMC5501176
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jdiacomp.2017.04.012
Energy sensing pathways: Bridging type 2 diabetes and colorectal cancer?
Abstract
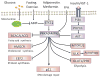
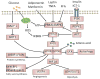
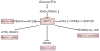
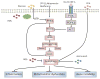
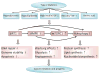
The recently rapid increase of obesity and type 2 diabetes mellitus has caused great burden to our society. A positive association between type 2 diabetes and risk of colorectal cancer has been reported by increasing epidemiological studies. The molecular mechanism of this connection remains elusive. However, type 2 diabetes may result in abnormal carbohydrate and lipid metabolism, high levels of circulating insulin, insulin growth factor-1, and adipocytokines, as well as chronic inflammation. All these factors could lead to the alteration of energy sensing pathways such as the AMP activated kinase (PRKA), mechanistic (mammalian) target of rapamycin (mTOR), SIRT1, and autophagy signaling pathways. The resulted impaired SIRT1 and autophagy signaling pathway could increase the risk of gene mutation and cancer genesis by decreasing genetic stability and DNA mismatch repair. The dysregulated mTOR and PRKA pathway could remodel cell metabolism during the growth and metastasis of cancer in order for the cancer cell to survive the unfavorable microenvironment such as hypoxia and low blood supply. Moreover, these pathways may be coupling metabolic and epigenetic alterations that are central to oncogenic transformation. Further researches including molecular pathologic epidemiologic studies are warranted to better address the precise links between these two important diseases.
Keywords: Biomarker; Carcinoma; Colon; Energy balance; Molecular pathologic epidemiology; PRKA.
Copyright © 2017 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Tsilidis KK, Kasimis JC, Lopez DS, et al. Type 2 diabetes and cancer: umbrella review of meta-analyses of observational studies. BMJ. 2015;350:g7607. - PubMed
-
- Jaacks LM, Siegel KR, Gujral UP, Narayan KM. Type 2 diabetes: A 21st century epidemic. Best Pract Res Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2016;30:331–343. - PubMed
-
- Shi Y, Hu FB. The global implications of diabetes and cancer. Lancet. 2014;383:1947–1948. - PubMed
-
- La Vecchia C, D'Avanzo B, Negri E, Franceschi S. History of selected diseases and the risk of colorectal cancer. Eur J Cancer. 1991;27:582–586. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

