Bipotent progenitors as embryonic origin of retinal stem cells
- PMID: 28465291
- PMCID: PMC5461025
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.201611057
Bipotent progenitors as embryonic origin of retinal stem cells
Abstract
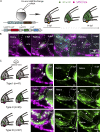
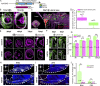
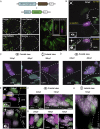
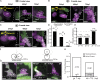
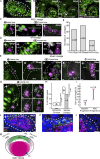
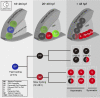
In lower vertebrates, retinal stem cells (RSCs) capable of producing all retinal cell types are a resource for retinal tissue growth throughout life. However, the embryonic origin of RSCs remains largely elusive. Using a Zebrabow-based clonal analysis, we characterized the RSC niche in the ciliary marginal zone of zebrafish retina and illustrate that blood vessels associated with RSCs are required for the maintenance of actively proliferating RSCs. Full lineage analysis of RSC progenitors reveals lineage patterns of RSC production. Moreover, in vivo lineage analysis demonstrates that these RSC progenitors are the direct descendants of a set of bipotent progenitors in the medial epithelial layer of developing optic vesicles, suggesting the involvement of the mixed-lineage states in the RSC lineage specification.
© 2017 Tang et al.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Molecular characterization of retinal stem cells and their niches in adult zebrafish.BMC Dev Biol. 2006 Jul 26;6:36. doi: 10.1186/1471-213X-6-36. BMC Dev Biol. 2006. PMID: 16872490 Free PMC article.
-
Unifying developmental programs for embryonic and postembryonic neurogenesis in the zebrafish retina.Development. 2020 Jun 19;147(12):dev185660. doi: 10.1242/dev.185660. Development. 2020. PMID: 32467236
-
dazed gene is necessary for late cell type development and retinal cell maintenance in the zebrafish retina.Dev Dyn. 2005 Jun;233(2):680-94. doi: 10.1002/dvdy.20375. Dev Dyn. 2005. PMID: 15844196
-
A moving wave patterns the cone photoreceptor mosaic array in the zebrafish retina.Int J Dev Biol. 2004;48(8-9):935-45. doi: 10.1387/ijdb.041873pr. Int J Dev Biol. 2004. PMID: 15558484 Review.
-
The 'definitive' (and 'primitive') guide to zebrafish hematopoiesis.Oncogene. 2004 Sep 20;23(43):7233-46. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1207943. Oncogene. 2004. PMID: 15378083 Review.
Cited by
-
Fgf8P2A-3×GFP/+: A New Genetic Mouse Model for Specifically Labeling and Sorting Cochlear Inner Hair Cells.Neurosci Bull. 2023 Dec;39(12):1762-1774. doi: 10.1007/s12264-023-01069-y. Epub 2023 May 26. Neurosci Bull. 2023. PMID: 37233921 Free PMC article.
-
Single-cell atlas comparison across vertebrates reveals auditory cell evolution and mechanisms for hair cell regeneration.Commun Biol. 2024 Dec 19;7(1):1648. doi: 10.1038/s42003-024-07335-7. Commun Biol. 2024. PMID: 39702452 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of the Potential Effects of Retinol and Alginate/Gelatin-Based Scaffolds on Differentiation Capacity of Mouse Mesenchymal Stem Cells (MSCs) into Retinal Cells.Int J Stem Cells. 2022 May 30;15(2):183-194. doi: 10.15283/ijsc21062. Int J Stem Cells. 2022. PMID: 34711698 Free PMC article.
-
Retinal Stem Cell 'Retirement Plans': Growth, Regulation and Species Adaptations in the Retinal Ciliary Marginal Zone.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Jun 18;22(12):6528. doi: 10.3390/ijms22126528. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34207050 Free PMC article. Review.
-
dnmt1 function is required to maintain retinal stem cells within the ciliary marginal zone of the zebrafish eye.Sci Rep. 2020 Jul 9;10(1):11293. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-68016-z. Sci Rep. 2020. PMID: 32647199 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

