Million Hearts: Description of the National Surveillance and Modeling Methodology Used to Monitor the Number of Cardiovascular Events Prevented During 2012-2016
- PMID: 28465301
- PMCID: PMC5524118
- DOI: 10.1161/JAHA.117.006021
Million Hearts: Description of the National Surveillance and Modeling Methodology Used to Monitor the Number of Cardiovascular Events Prevented During 2012-2016
Abstract
Background: This study describes the national surveillance and modeling methodology developed to monitor achievement of the Million Hearts initiative's aim of preventing 1 million acute myocardial infarctions, strokes, and other related cardiovascular events during 2012-2016.
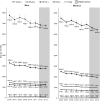
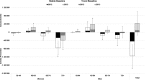
Methods and results: We calculate sex- and age-specific cardiovascular event rates (combination of emergency department, hospitalization, and death events) among US adults aged ≥18 from 2006 to 2011 and, based on log-linear models fitted to the rates, calculate their annual percent change. We describe 2 baseline strategies to be used to compare observed versus expected event totals during 2012-2016: (1) stable baselines assume no rate changes, with modeled 2011 rates held constant through 2016; and (2) trend baselines assume 2006-2011 rate trends will continue, with the annual percent changes applied to the modeled 2011 rates to calculate expected 2012-2016 rates. Events prevented estimates during 2012-2013 were calculated using available data: 115 210 (95% CI, 60 858, 169 562) events were prevented using stable baselines and an excess of 43 934 (95% CI, -14 264, 102 132) events occurred using trend baselines. Women aged ≥75 had the most events prevented (stable, 76 242 [42 067, 110 417]; trend, 39 049 [1901, 76 197]). Men aged 45 to 64 had the greatest number of excess events (stable, 22 912 [95% CI, 855, 44 969]; trend, 38 810 [95% CI, 15 567, 62 053]).
Conclusions: Around 115 000 events were prevented during the initiative's first 2 years compared with what would have occurred had 2011 rates remained stable. Recent flattening or reversals in some event rate trends were observed supporting intensifying national action to prevent cardiovascular events.
Keywords: Million Hearts; cardiovascular disease prevention; heart disease; hospitalization; mortality; myocardial infarction; stroke.
© 2017 The Authors. Published on behalf of the American Heart Association, Inc., by Wiley.
Figures

References
-
- Mozaffarian D, Benjamin EJ, Go AS, Arnett DK, Blaha MJ, Cushman M, Das SR, de Ferranti S, Després JP, Fullerton HJ, Howard VJ, Huffman MD, Isasi CR, Jiménez MC, Judd SE, Kissela BM, Lichtman JH, Lisabeth LD, Liu S, Mackey RH, Magid DJ, McGuire DK, Mohler ER III, Moy CS, Muntner P, Mussolino ME, Nasir K, Neumar RW, Nichol G, Palaniappan L, Pandey DK, Reeves MJ, Rodriguez CJ, Rosamond W, Sorlie PD, Stein J, Towfighi A, Turan TN, Virani SS, Woo D, Yeh RW, Turner MB; American Heart Association Statistics Committee; Stroke Statistics Subcommittee . Heart disease and stroke statistics—2016 update: a report from the American Heart Association. Circulation. 2016;133:e38–e360. - PubMed
-
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention . Prevalence and most common causes of disability among adults—United States, 2005. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2009;58:421–426. - PubMed
-
- Murphy SL, Kochanek KD, Xu JQ, Arias E. Mortality in the United States, 2014. NCHS data brief, no 229. Hyattsville, MD: National Center for Health Statistics; 2015. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

