Development of the hypothalamus: conservation, modification and innovation
- PMID: 28465334
- PMCID: PMC5450842
- DOI: 10.1242/dev.139055
Development of the hypothalamus: conservation, modification and innovation
Abstract
The hypothalamus, which regulates fundamental aspects of physiological homeostasis and behavior, is a brain region that exhibits highly conserved anatomy across vertebrate species. Its development involves conserved basic mechanisms of induction and patterning, combined with a more plastic process of neuronal fate specification, to produce brain circuits that mediate physiology and behavior according to the needs of each species. Here, we review the factors involved in the induction, patterning and neuronal differentiation of the hypothalamus, highlighting recent evidence that illustrates how changes in Wnt/β-catenin signaling during development may lead to species-specific form and function of this important brain structure.
Keywords: Adult neurogenesis; Evolution; Hypothalamus; Wnt.
© 2017. Published by The Company of Biologists Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interestsThe authors declare no competing or financial interests.
Figures


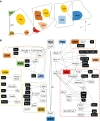


References
-
- Acampora D., Postiglione M. P., Avantaggiato V., Di Bonito M., Vaccarino F. M., Michaud J. and Simeone A. (1999). Progressive impairment of developing neuroendocrine cell lineages in the hypothalamus of mice lacking the Orthopedia gene. Genes Dev. 13, 2787-2800. 10.1101/gad.13.21.2787 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Anthwal N., Pelling M., Claxton S., Mellitzer G., Collin C., Kessaris N., Richardson W. D., Gradwohl G. and Ang S.-L. (2013). Conditional deletion of neurogenin-3 using Nkx2.1iCre results in a mouse model for the central control of feeding, activity and obesity. Dis. Model. Mech. 6, 1133-1145. 10.1242/dmm.011916 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

