Structural variants caused by Alu insertions are associated with risks for many human diseases
- PMID: 28465436
- PMCID: PMC5441760
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1704117114
Structural variants caused by Alu insertions are associated with risks for many human diseases
Abstract
Interspersed repeat sequences comprise much of our DNA, although their functional effects are poorly understood. The most commonly occurring repeat is the Alu short interspersed element. New Alu insertions occur in human populations, and have been responsible for several instances of genetic disease. In this study, we sought to determine if there are instances of polymorphic Alu insertion variants that function in a common variant, common disease paradigm. We cataloged 809 polymorphic Alu elements mapping to 1,159 loci implicated in disease risk by genome-wide association study (GWAS) (P < 10-8). We found that Alu insertion variants occur disproportionately at GWAS loci (P = 0.013). Moreover, we identified 44 of these Alu elements in linkage disequilibrium (r2 > 0.7) with the trait-associated SNP. This figure represents a >20-fold increase in the number of polymorphic Alu elements associated with human phenotypes. This work provides a broader perspective on how structural variants in repetitive DNAs may contribute to human disease.
Keywords: Alu; GWAS; causative variant; interspersed repeats; structural variant.
Conflict of interest statement
J.H. was a PhD trainee of J.D.B. (graduation date 2005). J.H. was a middle author on a single paper from J.D.B. in the past 4 years, on an unrelated project; its publication was delayed until 2014. All other authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
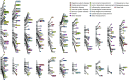
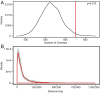
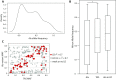


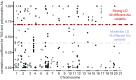
References
-
- Lander ES, et al. International Human Genome Sequencing Consortium Initial sequencing and analysis of the human genome. Nature. 2001;409:860–921. - PubMed
-
- Smit AFA, Hubley R, Green P. 2015 RepeatMasker Open-4.0. Available at www.repeatmasker.org. Accessed April 26, 2017.
-
- Kazazian HH, Jr, et al. Haemophilia A resulting from de novo insertion of L1 sequences represents a novel mechanism for mutation in man. Nature. 1988;332:164–166. - PubMed
-
- Sukarova E, Dimovski AJ, Tchacarova P, Petkov GH, Efremov GD. An Alu insert as the cause of a severe form of hemophilia A. Acta Haematol. 2001;106:126–129. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

