Mechanism of signal propagation in Physarum polycephalum
- PMID: 28465441
- PMCID: PMC5441820
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1618114114
Mechanism of signal propagation in Physarum polycephalum
Abstract
Complex behaviors are typically associated with animals, but the capacity to integrate information and function as a coordinated individual is also a ubiquitous but poorly understood feature of organisms such as slime molds and fungi. Plasmodial slime molds grow as networks and use flexible, undifferentiated body plans to forage for food. How an individual communicates across its network remains a puzzle, but Physarum polycephalum has emerged as a novel model used to explore emergent dynamics. Within P. polycephalum, cytoplasm is shuttled in a peristaltic wave driven by cross-sectional contractions of tubes. We first track P. polycephalum's response to a localized nutrient stimulus and observe a front of increased contraction. The front propagates with a velocity comparable to the flow-driven dispersion of particles. We build a mathematical model based on these data and in the aggregate experiments and model identify the mechanism of signal propagation across a body: The nutrient stimulus triggers the release of a signaling molecule. The molecule is advected by fluid flows but simultaneously hijacks flow generation by causing local increases in contraction amplitude as it travels. The molecule is initiating a feedback loop to enable its own movement. This mechanism explains previously puzzling phenomena, including the adaptation of the peristaltic wave to organism size and P. polycephalum's ability to find the shortest route between food sources. A simple feedback seems to give rise to P. polycephalum's complex behaviors, and the same mechanism is likely to function in the thousands of additional species with similar behaviors.
Keywords: Taylor dispersion; acellular slime mold; behavior; transport network.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures




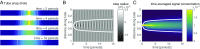

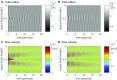

References
-
- Bonner JT. The Evolution of Culture in Animals. Princeton Univ Press; Princeton: 1980.
-
- Berg HC. Chemotaxis in bacteria. Ann Rev Biophys Bioeng. 1975;4:119–136. - PubMed
-
- Boddy L, Hynes J, Bebber DP, Fricker MD. Saprotrophic cord systems: Dispersal mechanisms in space and time. Mycoscience. 2009;50:9–19.
-
- Nakagaki T, Yamada H, Tóth A. Maze-solving by an amoeboid organism. Nature. 2000;407:470. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

