Characteristics associated with requests by pathologists for second opinions on breast biopsies
- PMID: 28465449
- PMCID: PMC5849252
- DOI: 10.1136/jclinpath-2016-204231
Characteristics associated with requests by pathologists for second opinions on breast biopsies
Abstract
Aims: Second opinions in pathology improve patient safety by reducing diagnostic errors, leading to more appropriate clinical treatment decisions. Little objective data are available regarding the factors triggering a request for second opinion despite second opinion consultations being part of the diagnostic system of pathology. Therefore we sought to assess breast biopsy cases and interpreting pathologists characteristics associated with second opinion requests.
Methods: Collected pathologist surveys and their interpretations of 60 test set cases were used to explore the relationships between case characteristics, pathologist characteristics and case perceptions, and requests for second opinions. Data were evaluated by logistic regression and generalised estimating equations.
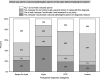
Results: 115 pathologists provided 6900 assessments; pathologists requested second opinions on 70% (4827/6900) of their assessments 36% (1731/4827) of these would not have been required by policy. All associations between case characteristics and requesting second opinions were statistically significant, including diagnostic category, breast density, biopsy type, and number of diagnoses noted per case. Exclusive of institutional policies, pathologists wanted second opinions most frequently for atypia (66%) and least frequently for invasive cancer (20%). Second opinion rates were higher when the pathologist had lower assessment confidence, in cases with higher perceived difficulty, and cases with borderline diagnoses.
Conclusions: Pathologists request second opinions for challenging cases, particularly those with atypia, high breast density, core needle biopsies, or many co-existing diagnoses. Further studies should evaluate whether the case characteristics identified in this study could be used as clinical criteria to prompt system-level strategies for mandating second opinions.
Keywords: BREAST CANCER; BREAST PATHOLOGY; DIAGNOSIS; LABORATORY MANAGEMENT.
Published by the BMJ Publishing Group Limited. For permission to use (where not already granted under a licence) please go to http://www.bmj.com/company/products-services/rights-and-licensing/.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: None declared.
Figures
References
-
- Middleton LP, Feeley TW, Albright HW, et al. Second-opinion pathologic review is a patient safety mechanism that helps reduce error and decrease waste. J Oncol Pract. 2014;10:275–80. - PubMed
-
- Manion E, Cohen M, Weydert J. Mandatory second opinion in surgical pathology referral material: clinical consequences of major disagreements. Am J Surg Path. 2008;32:732–7. - PubMed
-
- Kronz J, Westra W, Epstein J. Mandatory second opinion surgical pathology at a large referral hospital. Cancer. 1999;86:2426–35. - PubMed
-
- Gupta D, Layfield L. Prevalence of inter-institutional anatomic pathology slide review. Am J Surg Pathol. 2000;24:280–4. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical