Inflammatory signals from photoreceptor modulate pathological retinal angiogenesis via c-Fos
- PMID: 28465464
- PMCID: PMC5461000
- DOI: 10.1084/jem.20161645
Inflammatory signals from photoreceptor modulate pathological retinal angiogenesis via c-Fos
Abstract
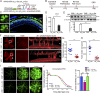
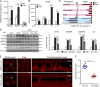
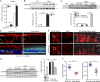
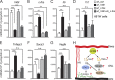
Pathological neovessels growing into the normally avascular photoreceptors cause vision loss in many eye diseases, such as age-related macular degeneration and macular telangiectasia. Ocular neovascularization is strongly associated with inflammation, but the source of inflammatory signals and the mechanisms by which these signals regulate the disruption of avascular privilege in photoreceptors are unknown. In this study, we found that c-Fos, a master inflammatory regulator, was increased in photoreceptors in a model of pathological blood vessels invading photoreceptors: the very low-density lipoprotein receptor-deficient (Vldlr-/- ) mouse. Increased c-Fos induced inflammatory cytokines interleukin 6 (IL-6) and tumor necrosis factor (TNF), leading to activation of signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 (STAT3) and increased TNFα-induced protein 3 (TNFAIP3) in Vldlr-/- photoreceptors. IL-6 activated the STAT3/vascular endothelial growth factor A (VEGFA) pathway directly, and elevated TNFAIP3 suppressed SOCS3 (suppressor of cytokine signaling 3)-activated STAT3/VEGFA indirectly. Inhibition of c-Fos using photoreceptor-specific AAV (adeno-associated virus)-hRK (human rhodopsin kinase)-sh_c-fos or a chemical inhibitor substantially reduced the pathological neovascularization and rescued visual function in Vldlr-/- mice. These findings suggested that the photoreceptor c-Fos controls blood vessel growth into the normally avascular photoreceptor layer through the inflammatory signal-induced STAT3/VEGFA pathway.
© 2017 Sun et al.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Prolonged blockade of VEGF receptors does not damage retinal photoreceptors or ganglion cells.J Cell Physiol. 2010 Jul;224(1):262-72. doi: 10.1002/jcp.22129. J Cell Physiol. 2010. PMID: 20232317 Free PMC article.
-
Photoreceptor avascular privilege is shielded by soluble VEGF receptor-1.Elife. 2013 Jun 18;2:e00324. doi: 10.7554/eLife.00324. Elife. 2013. PMID: 23795287 Free PMC article.
-
Photoreceptors inhibit pathological retinal angiogenesis through transcriptional regulation of Adam17 via c-Fos.Angiogenesis. 2024 Aug;27(3):379-395. doi: 10.1007/s10456-024-09912-0. Epub 2024 Mar 14. Angiogenesis. 2024. PMID: 38483712 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting Neurovascular Interaction in Retinal Disorders.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Feb 22;21(4):1503. doi: 10.3390/ijms21041503. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32098361 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Endothelial tip cells in ocular angiogenesis: potential target for anti-angiogenesis therapy.J Histochem Cytochem. 2013 Feb;61(2):101-15. doi: 10.1369/0022155412467635. Epub 2012 Oct 23. J Histochem Cytochem. 2013. PMID: 23092791 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Transcriptional and Distributional Profiling of Microglia in Retinal Angiomatous Proliferation.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Mar 22;23(7):3443. doi: 10.3390/ijms23073443. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35408803 Free PMC article.
-
Oxidative stress in the retina: implications for Retinopathy of Prematurity.Curr Opin Toxicol. 2018 Feb;7:102-109. doi: 10.1016/j.cotox.2017.11.008. Epub 2017 Nov 20. Curr Opin Toxicol. 2018. PMID: 35784947 Free PMC article.
-
PPARα-Dependent Effects of Palmitoylethanolamide Against Retinal Neovascularization and Fibrosis.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2020 Apr 9;61(4):15. doi: 10.1167/iovs.61.4.15. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2020. PMID: 32298438 Free PMC article.
-
GWAS on retinal vasculometry phenotypes.PLoS Genet. 2023 Feb 9;19(2):e1010583. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1010583. eCollection 2023 Feb. PLoS Genet. 2023. PMID: 36757925 Free PMC article.
-
Photoreceptor-targeted extracellular vesicles-mediated delivery of Cul7 siRNA for retinal degeneration therapy.Theranostics. 2024 Aug 12;14(13):4916-4932. doi: 10.7150/thno.99484. eCollection 2024. Theranostics. 2024. PMID: 39267786 Free PMC article.
References
-
- al-Ubaidi M.R., Font R.L., Quiambao A.B., Keener M.J., Liou G.I., Overbeek P.A., and Baehr W.. 1992. Bilateral retinal and brain tumors in transgenic mice expressing simian virus 40 large T antigen under control of the human interphotoreceptor retinoid-binding protein promoter. J. Cell Biol. 119:1681–1687. 10.1083/jcb.119.6.1681 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Angel P., and Karin M.. 1991. The role of Jun, Fos and the AP-1 complex in cell-proliferation and transformation. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 1072:129–157. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

