The Rational Design of Therapeutic Peptides for Aminopeptidase N using a Substrate-Based Approach
- PMID: 28465619
- PMCID: PMC5431086
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-017-01542-5
The Rational Design of Therapeutic Peptides for Aminopeptidase N using a Substrate-Based Approach
Abstract
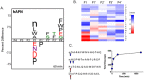
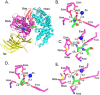
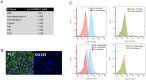
The M1 family of metalloproteases represents a large number of exopeptidases that cleave single amino acid residues from the N-terminus of peptide substrates. One member of this family that has been well studied is aminopeptidase N (APN), a multifunctional protease known to cleave biologically active peptides and aide in coronavirus entry. The proteolytic activity of APN promotes cancer angiogenesis and metastasis making it an important target for cancer therapy. To understand the substrate specificity of APN for the development of targeted inhibitors, we used a global substrate profiling method to determine the P1-P4' amino acid preferences. The key structural features of the APN pharmacophore required for substrate recognition were elucidated by x-ray crystallography. By combining these substrate profiling and structural data, we were able to design a selective peptide inhibitor of APN that was an effective therapeutic both in vitro and in vivo against APN-expressing prostate cancer models.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures

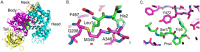
Similar articles
-
Design of Aminopeptidase N Inhibitors as Anti-cancer Agents.J Med Chem. 2018 Aug 9;61(15):6468-6490. doi: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.7b00782. Epub 2018 Apr 16. J Med Chem. 2018. PMID: 29630364 Review.
-
The effect of different species aminopeptidase N structure on the activity screening of aminopeptidase N inhibitor.Biol Pharm Bull. 2010;33(10):1658-65. doi: 10.1248/bpb.33.1658. Biol Pharm Bull. 2010. PMID: 20930372
-
Progress in the development of aminopeptidase N (APN/CD13) inhibitors.Curr Med Chem Anticancer Agents. 2005 May;5(3):281-301. doi: 10.2174/1568011053765949. Curr Med Chem Anticancer Agents. 2005. PMID: 15992355 Review.
-
Recent advance in aminopeptidase N (APN/CD13) inhibitor research.Curr Med Chem. 2011;18(32):5011-21. doi: 10.2174/092986711797535155. Curr Med Chem. 2011. PMID: 22050749 Review.
-
Exploring the structural aspects of ureido-amino acid-based APN inhibitors: a validated comparative multi-QSAR modelling study.SAR QSAR Environ Res. 2020 May 3;31(5):325-345. doi: 10.1080/1062936X.2020.1734080. Epub 2020 Mar 16. SAR QSAR Environ Res. 2020. PMID: 32174187
Cited by
-
Gut Digestive Function and Microbiome after Correction of Experimental Dysbiosis in Rats by Indigenous Bifidobacteria.Microorganisms. 2021 Mar 4;9(3):522. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms9030522. Microorganisms. 2021. PMID: 33806341 Free PMC article.
-
Neutral metalloaminopeptidases APN and MetAP2 as newly discovered anticancer molecular targets of actinomycin D and its simple analogs.Oncotarget. 2018 Jun 29;9(50):29365-29378. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.25532. eCollection 2018 Jun 29. Oncotarget. 2018. PMID: 30034623 Free PMC article.
-
Quantitative Multiplex Substrate Profiling of Peptidases by Mass Spectrometry.Mol Cell Proteomics. 2019 May;18(5):968-981. doi: 10.1074/mcp.TIR118.001099. Epub 2019 Jan 31. Mol Cell Proteomics. 2019. PMID: 30705125 Free PMC article.
-
ERAP1 binds peptide C-termini of different sequences and/or lengths by a common recognition mechanism.Immunobiology. 2021 Jul;226(4):152112. doi: 10.1016/j.imbio.2021.152112. Epub 2021 Jul 4. Immunobiology. 2021. PMID: 34247019 Free PMC article.
-
Current state of in vivo panning technologies: Designing specificity and affinity into the future of drug targeting.Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2018 May;130:39-49. doi: 10.1016/j.addr.2018.06.015. Epub 2018 Jun 28. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2018. PMID: 29964079 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

