Echocardiographic Assessment of Heart Valve Prostheses
- PMID: 28465917
- PMCID: PMC5353566
- DOI: 10.4103/2211-4122.147201
Echocardiographic Assessment of Heart Valve Prostheses
Abstract
Patients submitted to valve replacement with mechanical or biological prosthesis, may present symptoms related either to valvular malfunction or ventricular dysfunction from other causes. Because a clinical examination is not sufficient to evaluate a prosthetic valve, several diagnostic methods have been proposed to assess the functional status of a prosthetic valve. This review provides an overview of echocardiographic and Doppler techniques useful in evaluation of prosthetic heart valves. Compared to native valves, echocardiographic evaluation of prosthetic valves is certainly more complex, both for the examination and the interpretation. Echocardiography also allows discriminating between intra- and/or peri-prosthetic regurgitation, present in the majority of mechanical valves. Transthoracic echocardiography (TTE) requires different angles of the probe with unconventional views. Transesophageal echocardiography (TEE) is the method of choice in presence of technical difficulties. Three-dimensional (3D)-TEE seems to be superior to 2D-TEE, especially in the assessment of paravalvular leak regurgitation (PVL) that it provides improved localization and analysis of the PVL size and shape.
Keywords: 3D transesophageal echocardiography; Prosthetic heart valves; transesophageal echocardiography; transthoracic echocardiography.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interest: None declared.
Figures

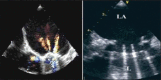

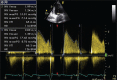

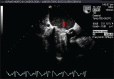
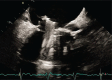
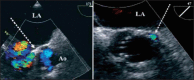
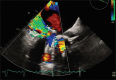
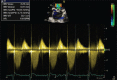


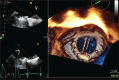
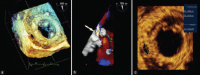
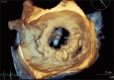

References
-
- Otto Catherine M. Pibarot P, Dumesnil JG, editors. Textbook of Clinical Echocardiography. 2013;1(Chapter 25):470–493.
-
- Pibarot P, Dumesnil JG. Prosthetic heart valves: Selection of the optimal prosthesis and long-term management. Circulation. 2009;119:1034–48. - PubMed
-
- Cribier A, Eltchaninoff H, Tron C, Bauer F, Agatiello C, Sebagh L, et al. Early experience with percutaneous transcatheter implantation of heart valve prosthesis for the treatment of end-stage inoperable patients with calcific aortic stenosis. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2004;43:698–703. - PubMed
-
- Webb JG, Chandavimol M, Thompson CR, Ricci DR, Carere RG, Munt BI, et al. Percutaneous aortic valve implantation retrograde from the femoral artery. Circulation. 2006;113:842–50. - PubMed
-
- Grube E, Schuler G, Buellesfeld L, Gerckens U, Linke A, Wenaweser P, et al. Percutaneous aortic valve replacement for severe aortic stenosis in high-risk patients using the second- and current third generation-expanding CoreValve prosthesis: Device success and 30-day clinical outcome. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2007;50:69–76. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
