Efficacy of Magnetic Sphincter Augmentation versus Nissen Fundoplication for Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease in Short Term: A Meta-Analysis
- PMID: 28466002
- PMCID: PMC5390656
- DOI: 10.1155/2017/9596342
Efficacy of Magnetic Sphincter Augmentation versus Nissen Fundoplication for Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease in Short Term: A Meta-Analysis
Abstract
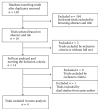
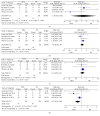
Background. The efficacy of Magnetic Sphincter Augmentation (MSA) and its outcomes for Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD) are uncertain. Therefore, we aimed to summarize and analyze the efficacy of two treatments for GERD. Methods. The meta-analysis search was performed, using four databases. All studies from 2005 to 2016 were included. Pooled effect was calculated using either the fixed or random effects model. Results. A total of 4 trials included 624 patients and aimed to evaluate the differences in proton-pump inhibitor use, complications, and adverse events. MSA had a shorter operative time (MSA and NF: RR = -18.80, 95% CI: -24.57 to -13.04, and P = 0.001) and length of stay (RR = -14.21, 95% CI: -24.18 to -4.23, and P = 0.005). Similar proton-pump inhibitor use, complication (P = 0.19), and severe dysphagia for dilation were shown in both groups. Although there is no difference between the MSA and NF in the number of adverse events, the incidence of postoperative gas or bloating (RR = 0.71, 95% CI: 0.54-0.94, and P = 0.02) showed significantly different results. However, there is no significant difference in ability to belch and ability to vomit. Conclusions. MSA can be recommended as an alternative treatment for GERD according to their short-term studies, especially in main-features of gas-bloating, due to shorter operative time and less complication of gas or bloating.
Figures


Similar articles
-
LINX® magnetic esophageal sphincter augmentation versus Nissen fundoplication for gastroesophageal reflux disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Surg Endosc. 2017 Aug;31(8):3078-3084. doi: 10.1007/s00464-016-5370-3. Epub 2016 Dec 15. Surg Endosc. 2017. PMID: 27981382
-
Laparoscopic magnetic sphincter augmentation versus fundoplication for gastroesophageal reflux disease: systematic review and pooled analysis.Dis Esophagus. 2019 Nov 13;32(9):doz031. doi: 10.1093/dote/doz031. Dis Esophagus. 2019. PMID: 31069388
-
Multi-institutional outcomes using magnetic sphincter augmentation versus Nissen fundoplication for chronic gastroesophageal reflux disease.Surg Endosc. 2016 Aug;30(8):3289-96. doi: 10.1007/s00464-015-4659-y. Epub 2015 Nov 5. Surg Endosc. 2016. PMID: 26541740
-
Laparoscopic Magnetic Sphincter Augmentation vs Laparoscopic Nissen Fundoplication: A Matched-Pair Analysis of 100 Patients.J Am Coll Surg. 2015 Jul;221(1):123-8. doi: 10.1016/j.jamcollsurg.2015.02.025. Epub 2015 Mar 5. J Am Coll Surg. 2015. PMID: 26095560
-
Charges, outcomes, and complications: a comparison of magnetic sphincter augmentation versus laparoscopic Nissen fundoplication for the treatment of GERD.Surg Endosc. 2016 Aug;30(8):3225-30. doi: 10.1007/s00464-015-4635-6. Epub 2015 Nov 5. Surg Endosc. 2016. PMID: 26541730
Cited by
-
Novel Surgical Treatments for Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease: Systematic Review of Magnetic Sphincter Augmentation and Electric Stimulation Therapy.Gastroenterology Res. 2018 Jun;11(3):161-173. doi: 10.14740/gr1024w. Epub 2018 May 31. Gastroenterology Res. 2018. PMID: 29915626 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Systematic review of the introduction and evaluation of magnetic augmentation of the lower oesophageal sphincter for gastro-oesophageal reflux disease.Br J Surg. 2020 Jan;107(1):44-55. doi: 10.1002/bjs.11391. Epub 2019 Dec 4. Br J Surg. 2020. PMID: 31800095 Free PMC article.
-
A comparative study of magnetic sphincter augmentation and Nissen fundoplication in the management of GERD.Hernia. 2024 Dec;28(6):2367-2374. doi: 10.1007/s10029-024-03172-z. Epub 2024 Oct 14. Hernia. 2024. PMID: 39400916 Free PMC article.
-
Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease in Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis: Viewer or Actor? To Treat or Not to Treat?Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2022 Aug 22;15(8):1033. doi: 10.3390/ph15081033. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36015181 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Magnetic sphincter augmentation: Optimal patient selection and referral care pathways.World J Gastrointest Endosc. 2019 Aug 16;11(8):472-476. doi: 10.4253/wjge.v11.i8.472. World J Gastrointest Endosc. 2019. PMID: 31523378 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Lord R. V. N., Demeester S. R., Peters J. H., et al. Hiatal Hernia, lower esophageal sphincter incompetence, and effectiveness of nissen fundoplication in the spectrum of gastroesophageal reflux disease. Journal of Gastrointestinal Surgery. 2009;13(4):602–610. doi: 10.1007/s11605-008-0754-x. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

