In Search of Sleep Biomarkers of Alzheimer's Disease: K-Complexes Do Not Discriminate between Patients with Mild Cognitive Impairment and Healthy Controls
- PMID: 28468235
- PMCID: PMC5447933
- DOI: 10.3390/brainsci7050051
In Search of Sleep Biomarkers of Alzheimer's Disease: K-Complexes Do Not Discriminate between Patients with Mild Cognitive Impairment and Healthy Controls
Abstract
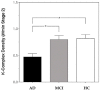
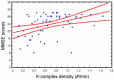
The K-complex (KC) is one of the hallmarks of Non-Rapid Eye Movement (NREM) sleep. Recent observations point to a drastic decrease of spontaneous KCs in Alzheimer's disease (AD). However, no study has investigated when, in the development of AD, this phenomenon starts. The assessment of KC density in mild cognitive impairment (MCI), a clinical condition considered a possible transitional stage between normal cognitive function and probable AD, is still lacking. The aim of the present study was to compare KC density in AD/MCI patients and healthy controls (HCs), also assessing the relationship between KC density and cognitive decline. Twenty amnesic MCI patients underwent a polysomnographic recording of a nocturnal sleep. Their data were compared to those of previously recorded 20 HCs and 20 AD patients. KCs during stage 2 NREM sleep were visually identified and KC densities of the three groups were compared. AD patients showed a significant KC density decrease compared with MCI patients and HCs, while no differences were observed between MCI patients and HCs. KC density was positively correlated with Mini-Mental State Examination (MMSE) scores. Our results point to the existence of an alteration of KC density only in a full-blown phase of AD, which was not observable in the early stage of the pathology (MCI), but linked with cognitive deterioration.
Keywords: Alzheimer’s disease; EEG; K-complexes; amnesic mild cognitive impairment; cognitive decline; sleep.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest regarding the publication of this paper. The founding sponsors had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, and in the decision to publish the results.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Sleep spindles, K-complexes, limb movements and sleep stage proportions may be biomarkers for amnestic mild cognitive impairment and Alzheimer's disease.Sleep Breath. 2020 Jun;24(2):637-651. doi: 10.1007/s11325-019-01970-9. Epub 2019 Nov 30. Sleep Breath. 2020. PMID: 31786748
-
The role of the sleep K-complex on the conversion from mild cognitive impairment to Alzheimer's disease.J Sleep Res. 2024 Feb;33(1):e14046. doi: 10.1111/jsr.14046. Epub 2023 Sep 18. J Sleep Res. 2024. PMID: 37718942
-
Parietal Fast Sleep Spindle Density Decrease in Alzheimer's Disease and Amnesic Mild Cognitive Impairment.Neural Plast. 2016;2016:8376108. doi: 10.1155/2016/8376108. Epub 2016 Mar 15. Neural Plast. 2016. PMID: 27066274 Free PMC article.
-
Neurofilament Light Chain as a Potential Biomarker in Plasma for Alzheimer's Disease and Mild Cognitive Impairment: A Systematic Review and a Meta-Analysis.J Integr Neurosci. 2023 Jun 30;22(4):85. doi: 10.31083/j.jin2204085. J Integr Neurosci. 2023. PMID: 37519166
-
Mini-Mental State Examination (MMSE) for the early detection of dementia in people with mild cognitive impairment (MCI).Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Jul 27;7(7):CD010783. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD010783.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021. PMID: 34313331 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
How non-rapid eye movement sleep and Alzheimer pathology are linked.World J Psychiatry. 2021 Nov 19;11(11):1027-1038. doi: 10.5498/wjp.v11.i11.1027. eCollection 2021 Nov 19. World J Psychiatry. 2021. PMID: 34888171 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Characteristics of macroscopic sleep structure in patients with mild cognitive impairment: a systematic review.Front Psychiatry. 2023 Jul 20;14:1212514. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2023.1212514. eCollection 2023. Front Psychiatry. 2023. PMID: 37547222 Free PMC article.
-
Spotlight on dream recall: the ages of dreams.Nat Sci Sleep. 2018 Jan 9;10:1-12. doi: 10.2147/NSS.S135762. eCollection 2018. Nat Sci Sleep. 2018. PMID: 29391838 Free PMC article. Review.
-
EEG alterations during wake and sleep in mild cognitive impairment and Alzheimer's disease.iScience. 2021 Apr 1;24(4):102386. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2021.102386. eCollection 2021 Apr 23. iScience. 2021. PMID: 33981973 Free PMC article.
-
Linking activity dyshomeostasis and sleep disturbances in Alzheimer disease.Nat Rev Neurosci. 2024 Apr;25(4):272-284. doi: 10.1038/s41583-024-00797-y. Epub 2024 Feb 19. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2024. PMID: 38374463 Review.
References
-
- Cummings J.L. Alzheimer’s disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2004;351:56–67. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

