Hypoxia Mediates Differential Response to Anti-EGFR Therapy in HNSCC Cells
- PMID: 28468237
- PMCID: PMC5454856
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms18050943
Hypoxia Mediates Differential Response to Anti-EGFR Therapy in HNSCC Cells
Abstract
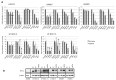
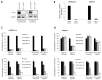
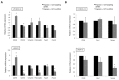
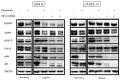
Despite advances in the head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC) treatment modalities, drug resistance and cancer recurrence are often reported. Hypoxia signaling through hypoxia-inducible factor 1 (HIF-1) promotes angiogenesis and metastasis by inducing epithelial-mesenchymal-transition (EMT). The aim of this study was to evaluate the impact of hypoxia on response to therapy as well as EMT and expression of stem cell markers in HNSCC cells. Five HNSCC cell lines (UT-SCC-2, UT-SCC-14, LK0412, LK0827, and LK0923) were selected for this study. The treatment sensitivity for radiation, cisplatin, cetuximab, and dasatinib was assessed by crystal violet assay. Gene expression of EMT and cancer stem cell (CSC) markers as well as protein level of EGFR signaling molecules were analyzed by qPCR and western blotting, respectively. Unlike UT-SCC-14 and LK0827, the LK0412 cell line became significantly more sensitive to cetuximab in hypoxic conditions. This cetuximab sensitivity was efficiently reversed after suppression of HIF-1α with siRNA. Additionally, hypoxia-induced EMT and expression of stem cell markers in HNSCC cells was partially revoked by treatment with cetuximab or knockdown of HIF-1α. In summary, our study shows that hypoxia might have a positive influence on the anti-EGFR therapy effectiveness in HNSCC. However, due to heterogeneity of HNSCC lesions, targeting HIF-1α may not be sufficient to mediate such a response. Further studies identifying a trait of hypoxia-specific response to cetuximab in HNSCC are advisable.
Keywords: HIF-1α; cancer stem cells (CSC); cetuximab; cisplatin; epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT); head and neck tumors; hypoxia; radiotherapy.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Cetuximab sensitivity of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma xenografts is associated with treatment-induced reduction in EGFR, pEGFR, and pSrc.J Oral Pathol Med. 2017 Oct;46(9):717-724. doi: 10.1111/jop.12545. Epub 2017 Jan 28. J Oral Pathol Med. 2017. PMID: 28036101
-
Dual Targeting of Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor and HER3 by MEHD7945A as Monotherapy or in Combination with Cisplatin Partially Overcomes Cetuximab Resistance in Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma Cell Lines.Cancer Biother Radiopharm. 2017 Sep;32(7):229-238. Cancer Biother Radiopharm. 2017. PMID: 28910149
-
EPR Oximetry of Cetuximab-Treated Head-and-Neck Tumours in a Mouse Model.Cell Biochem Biophys. 2017 Dec;75(3-4):299-309. doi: 10.1007/s12013-017-0814-5. Epub 2017 Jul 29. Cell Biochem Biophys. 2017. PMID: 28756482 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular targeted therapies in the management of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma: recent developments and perspectives.Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 2013 Mar;13(3):389-402. Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 2013. PMID: 23092267 Review.
-
Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Inhibition in Squamous Cell Carcinoma of the Head and Neck.Hematol Oncol Clin North Am. 2015 Dec;29(6):1011-32. doi: 10.1016/j.hoc.2015.07.007. Hematol Oncol Clin North Am. 2015. PMID: 26568545 Review.
Cited by
-
Treatment effects of the EGFR pathway drugs on head and neck cancer stem cells.Am J Cancer Res. 2022 Sep 15;12(9):4196-4210. eCollection 2022. Am J Cancer Res. 2022. PMID: 36225637 Free PMC article.
-
Meta-analysis of the effects of anti-epidermal growth factor receptor on recurrent/metastatic head and neck squamous cell carcinoma.Medicine (Baltimore). 2018 Dec;97(51):e13717. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000013717. Medicine (Baltimore). 2018. PMID: 30572506 Free PMC article.
-
Cetuximab and Paclitaxel Drug Response in Head and Neck Tumor Stem Cells.Biomolecules. 2025 Feb 28;15(3):352. doi: 10.3390/biom15030352. Biomolecules. 2025. PMID: 40149887 Free PMC article.
-
Shooting at Moving and Hidden Targets-Tumour Cell Plasticity and the Notch Signalling Pathway in Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinomas.Cancers (Basel). 2021 Dec 10;13(24):6219. doi: 10.3390/cancers13246219. Cancers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34944837 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hypoxia induces radioresistance, epithelial‑mesenchymal transition, cancer stem cell‑like phenotype and changes in genes possessing multiple biological functions in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma.Oncol Rep. 2022 Mar;47(3):58. doi: 10.3892/or.2022.8269. Epub 2022 Jan 21. Oncol Rep. 2022. PMID: 35059742 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

