A case report of novel mutation in PRF1 gene, which causes familial autosomal recessive hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis
- PMID: 28468610
- PMCID: PMC5415817
- DOI: 10.1186/s12881-017-0404-9
A case report of novel mutation in PRF1 gene, which causes familial autosomal recessive hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis
Abstract
Background: Hemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis (HLH) is a life-threatening immunodeficiency and multi-organ disease that affects people of all ages and ethnic groups. Common symptoms and signs of this disease are high fever, hepatosplenomegaly, and cytopenias. Familial form of HLH disease, which is an autosomal recessive hematological disorder is due to disease-causing mutations in several genes essential for NK and T-cell granule-mediated cytotoxic function. For an effective cytotoxic response from cytotoxic T lymphocyte or NK cell encountering an infected cell or tumor cell, different processes are required, including trafficking, docking, priming, membrane fusion, and entry of cytotoxic granules into the target cell leading to apoptosis. Therefore, genes involved in these steps play important roles in the pathogenesis of HLH disease which include PRF1, UNC13D (MUNC13-4), STX11, and STXBP2 (MUNC18-2).
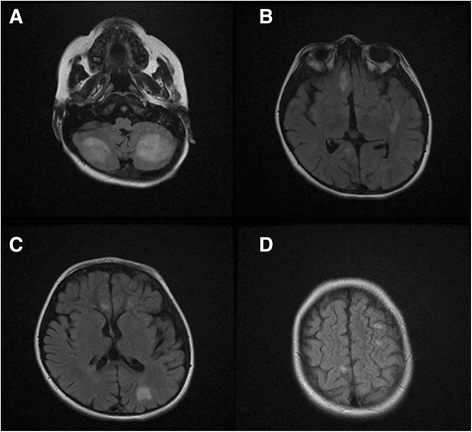
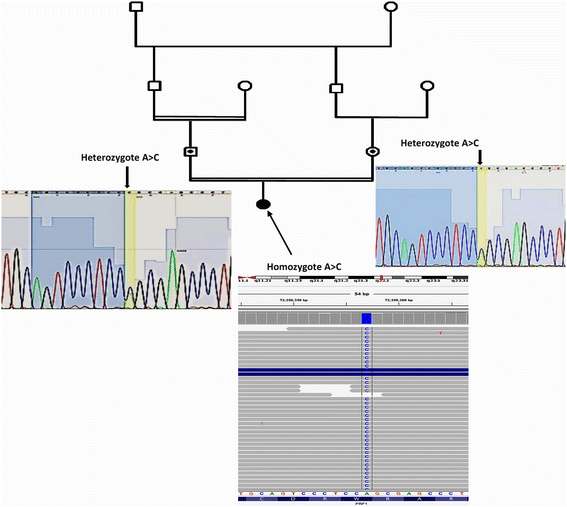
Case presentation: Here, we report a novel missense mutation in an 8-year-old boy suffered from hepatosplenomegaly, hepatitis, epilepsy and pancytopenia. The patient was born to a first-cousin parents with no previous documented disease in his parents. To identify mutated gene in the proband, Whole Exome Sequencing (WES) utilizing next generation sequencing was used on an Illumina HiSeq 2000 platform on DNA sample from the patient. Results showed a novel deleterious homozygous missense mutation in PRF1 gene (NM_001083116: exon3: c. 1120 T > G, p.W374G) in the patient and then using Sanger sequencing it was confirmed in the proband and his parents. Since his parents were heterozygous for the identified mutation, autosomal recessive pattern of inheritance was confirmed in the family.
Conclusions: Our study identified a rare new pathogenic missense mutation in PRF1 gene in patient with HLH disease and it is the first report of mutation in PRF1 in Iranian patients with this disease.
Keywords: Case report; Hemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis (HLH); Novel mutation; PRF1.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Familial Hemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis.2006 Mar 22 [updated 2024 Jun 6]. In: Adam MP, Feldman J, Mirzaa GM, Pagon RA, Wallace SE, Amemiya A, editors. GeneReviews® [Internet]. Seattle (WA): University of Washington, Seattle; 1993–2025. 2006 Mar 22 [updated 2024 Jun 6]. In: Adam MP, Feldman J, Mirzaa GM, Pagon RA, Wallace SE, Amemiya A, editors. GeneReviews® [Internet]. Seattle (WA): University of Washington, Seattle; 1993–2025. PMID: 20301617 Free Books & Documents. Review.
-
Ocular inflammation as the first presenting feature of PRF1-associated familial hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis, case report and review of literature.BMC Ophthalmol. 2025 Jul 7;25(1):394. doi: 10.1186/s12886-025-04226-1. BMC Ophthalmol. 2025. PMID: 40624627 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Familial Hemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis secondary to UNC13D mutation: a report of two cases.BMC Pediatr. 2022 Nov 19;22(1):667. doi: 10.1186/s12887-022-03746-9. BMC Pediatr. 2022. PMID: 36401200 Free PMC article.
-
Rare cause of Hemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis due to mutation in PRF1 and SH2D1A genes in two children - a case report with a review.BMC Pediatr. 2019 Mar 8;19(1):73. doi: 10.1186/s12887-019-1444-4. BMC Pediatr. 2019. PMID: 30849948 Free PMC article. Review.
-
UNC13D is the predominant causative gene with recurrent splicing mutations in Korean patients with familial hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis.Haematologica. 2010 Apr;95(4):622-6. doi: 10.3324/haematol.2009.016949. Epub 2009 Dec 16. Haematologica. 2010. PMID: 20015888 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Mechanistic Insights in Hemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis: Subsequent Acute Hepatic Failure in a Multiple Myeloma Patient Following Therapy with Ixazomib-Lenalidomide-Dexamethasone.J Pers Med. 2022 Apr 23;12(5):678. doi: 10.3390/jpm12050678. J Pers Med. 2022. PMID: 35629101 Free PMC article. Review.
-
RF1 Gene Mutation in Familial Hemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis 2: A Family Report and Literature Review.Pharmgenomics Pers Med. 2021 Dec 16;14:1637-1645. doi: 10.2147/PGPM.S326921. eCollection 2021. Pharmgenomics Pers Med. 2021. PMID: 34938098 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ishii E, Ohga S, Tanimura M, Imashuku S, Sako M, Mizutani S, Miyazaki S. Clinical and epidemiologic studies of familial hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis in Japan. Japan LCH study group. Med Pediatr Oncol. 1998;30(5):276–283. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1096-911X(199805)30:5<276::AID-MPO3>3.0.CO;2-C. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

