Punica granatum peel extracts: HPLC fractionation and LC MS analysis to quest compounds having activity against multidrug resistant bacteria
- PMID: 28468660
- PMCID: PMC5415797
- DOI: 10.1186/s12906-017-1766-4
Punica granatum peel extracts: HPLC fractionation and LC MS analysis to quest compounds having activity against multidrug resistant bacteria
Abstract
Background: Medicinal plants are rich source of traditional herbal medicine around the globe. Most of the plant's therapeutic properties are due to the presence of secondary bioactive compounds.
Methods: The present study analyzed the High Pressure Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) fractions of Puncia granatum (peel) extracts (aqueous, chloroform, ethanol and hexane) against multidrug resistant bacterial pathogens (Acinetobacter baumannii, Escherichia coli, Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Staphylococcus aureus). All the fractions having antibacterial activity was processed for bioactive compounds identification using LC MS/MS analysis.
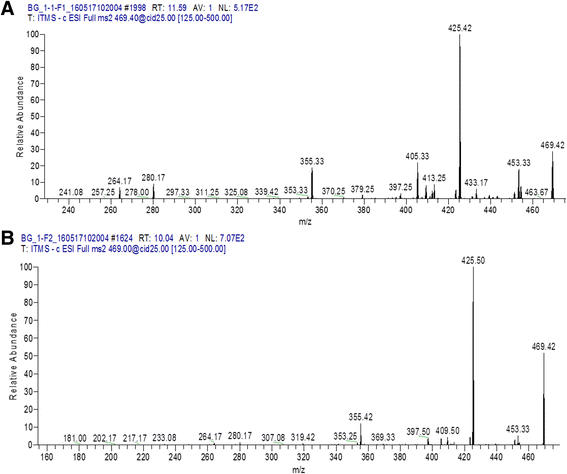
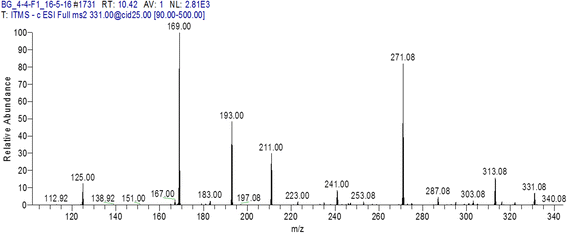
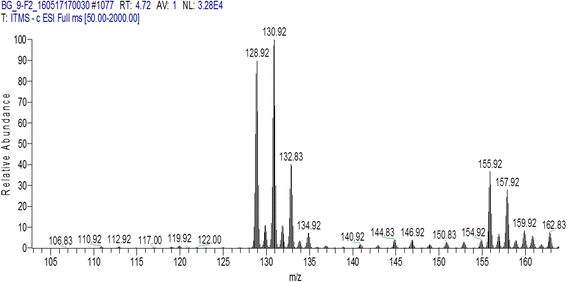
Results: Among total HPLC fractions (n = 30), 4 HPLC fractions of P. granatum (peel) showed potential activity against MDR pathogens. Fraction 1 (F1) and fraction 4 (F4) collected from aqueous extract showed maximum activity against P. aeruginosa. Fraction 2 (F2) of hexane showed antibacterial activity against three pathogens, while ethanol F4 exhibited antibacterial activity against A. baumannii. The active fractions were processed for LC MS/MS analysis to identify bioactive compounds. Valoneic acid dilactone (aqueous F1 and F4), Hexoside (ethanol F4) and Coumaric acid (hexane F2) were identified as bioactive compounds in HPLC fractions.
Conclusion: Puncia granatum peel extracts HPLC fractions exhibited potential inhibitory activity against MDR bacterial human pathogens. Several bioactive compounds were identified from the HPLC fractions. Further characterization of these compounds may be helpful to conclude it as therapeutic lead molecules against MDR pathogens.
Keywords: Anti-MDR activity; Coumaric acid; HPLC fractions; Hexoside; Puncia granatum peel extracts; Valoneic acid dilactone.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Glycyrrhiza glabra HPLC fractions: identification of Aldehydo Isoophiopogonone and Liquirtigenin having activity against multidrug resistant bacteria.BMC Complement Altern Med. 2018 May 2;18(1):140. doi: 10.1186/s12906-018-2207-8. BMC Complement Altern Med. 2018. PMID: 29720152 Free PMC article.
-
Alkanna tinctoria leaves extracts: a prospective remedy against multidrug resistant human pathogenic bacteria.BMC Complement Altern Med. 2015 Apr 23;15:127. doi: 10.1186/s12906-015-0646-z. BMC Complement Altern Med. 2015. PMID: 25902854 Free PMC article.
-
Fagonia cretica: Identification of compounds in bioactive gradient high performance liquid chromatography fractions against multidrug resistant human gut pathogens.Trop Biomed. 2022 Jun 1;39(2):185-190. doi: 10.47665/tb.39.2.006. Trop Biomed. 2022. PMID: 35838088
-
Therapeutic Potential of Punica granatum and Isolated Compounds: Evidence-Based Advances to Treat Bacterial Infections.Int J Microbiol. 2023 Dec 15;2023:4026440. doi: 10.1155/2023/4026440. eCollection 2023. Int J Microbiol. 2023. PMID: 38144901 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Liposoluble compounds from Ganoderma lipsiense grown on solid red rice medium with antiparasitic and antibacterial properties.Biotechnol Appl Biochem. 2020 Mar;67(2):180-185. doi: 10.1002/bab.1851. Epub 2019 Nov 27. Biotechnol Appl Biochem. 2020. PMID: 31710143 Review.
Cited by
-
Pharmacological activities and gas chromatography-mass spectrometry analysis for the identification of bioactive compounds from Justicia adhatoda L.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Sep 12;13:922388. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.922388. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 36172192 Free PMC article.
-
Scutellaria petiolata Hemsl. ex Lace & Prain (Lamiaceae).: A New Insight in Biomedical Therapies.Antioxidants (Basel). 2022 Jul 26;11(8):1446. doi: 10.3390/antiox11081446. Antioxidants (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35892648 Free PMC article.
-
Protective effects of Indigofera argentea against acetic acid-induced inflammatory bowel disease are mediated by modulating antioxidant and inflammatory mediators.Avicenna J Phytomed. 2025 Jan-Feb;15(2):964-980. doi: 10.22038/AJP.2024.24977. Avicenna J Phytomed. 2025. PMID: 40292264 Free PMC article.
-
Chemical composition, antioxidant and hepatoprotective activities of methanol extracts from leaves of Terminalia bellirica and Terminalia sericea (Combretaceae).PeerJ. 2019 Feb 27;7:e6322. doi: 10.7717/peerj.6322. eCollection 2019. PeerJ. 2019. PMID: 30834179 Free PMC article.
-
Electrospinning of antibacterial and anti-inflammatory Ag@hesperidin core-shell nanoparticles into nanofibers used for promoting infected wound healing.Regen Biomater. 2022 Feb 18;9:rbac012. doi: 10.1093/rb/rbac012. eCollection 2022. Regen Biomater. 2022. PMID: 35592139 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aisha A, Sarfraz RA, Mahmood A, Din MU. Chemical composition and in vitro antioxidant and antitumor activities of Eucalyptus camaldulensis Dehn. leaves. Ind Crop Prod. 2015;74:241–248. doi: 10.1016/j.indcrop.2015.04.059. - DOI
-
- Tahir HU, Sarfraz AR, Aisha A, Adil S. Chemical composition and anti-diabetic activity of essential oils obtained from two spices (Syzygium aromaticum and Cuminum cyminum) Int J Food Prop. 2016;19:2156–2164. doi: 10.1080/10942912.2015.1110166. - DOI
-
- Prajapati ND, Prajapati T. Sustainable cultivation of medicinal plants; Multi tier agriculture system-A new concept. Mathews CE, Van Holde KE, Ahern KG. Biochemistry. 3rd edn. USA: Benjamin Cummings. 1999.
-
- Zafar R. Medicinal plants of India. 15. Delhi: CBS Publication; 1994.
-
- Rauf A, Muhammad N, Khan A, Uddin N, Atif M, Barkatullah Antibacterial and Phytotoxic Profile of Selected Pakistani Medicinal Plants. World App Sci J. 2012;20:540–544.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

