Two alternate strategies for innate immunity to Epstein-Barr virus: One using NK cells and the other NK cells and γδ T cells
- PMID: 28468758
- PMCID: PMC5460997
- DOI: 10.1084/jem.20161017
Two alternate strategies for innate immunity to Epstein-Barr virus: One using NK cells and the other NK cells and γδ T cells
Abstract
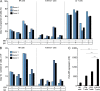
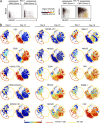
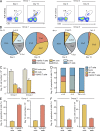
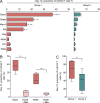
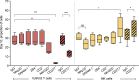
Most humans become infected with Epstein-Barr virus (EBV), which then persists for life. Infrequently, EBV infection causes infectious mononucleosis (IM) or Burkitt lymphoma (BL). Type I EBV infection, particularly type I BL, stimulates strong responses of innate immune cells. Humans respond to EBV in two alternative ways. Of 24 individuals studied, 13 made strong NK and γδ T cell responses, whereas 11 made feeble γδ T cell responses but stronger NK cell responses. The difference does not correlate with sex, HLA type, or previous exposure to EBV or cytomegalovirus. Cohorts of EBV+ children and pediatric IM patients include both group 1 individuals, with high numbers of γδ T cells, and group 2 individuals, with low numbers. The even balance of groups 1 and 2 in the human population points to both forms of innate immune response to EBV having benefit for human survival. Correlating these distinctive responses with the progress of EBV infection might facilitate the management of EBV-mediated disease.
© 2017 Djaoud et al.
Figures


References
-
- Amir A.D., Davis K.L., Tadmor M.D., Simonds E.F., Levine J.H., Bendall S.C., Shenfeld D.K., Krishnaswamy S., Nolan G.P., and Pe’er D.. 2013. viSNE enables visualization of high dimensional single-cell data and reveals phenotypic heterogeneity of leukemia. Nat. Biotechnol. 31:545–552. 10.1038/nbt.2594 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Béziat V., Dalgard O., Asselah T., Halfon P., Bedossa P., Boudifa A., Hervier B., Theodorou I., Martinot M., Debré P., et al. . 2012. CMV drives clonal expansion of NKG2C+ NK cells expressing self-specific KIRs in chronic hepatitis patients. Eur. J. Immunol. 42:447–457. 10.1002/eji.201141826 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Bukowski J.F., Morita C.T., and Brenner M.B.. 1994. Recognition and destruction of virus-infected cells by human gamma delta CTL. J. Immunol. 153:5133–5140. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

