Pervasive Behavioral Effects of MicroRNA Regulation in Drosophila
- PMID: 28468905
- PMCID: PMC5500149
- DOI: 10.1534/genetics.116.195776
Pervasive Behavioral Effects of MicroRNA Regulation in Drosophila
Abstract
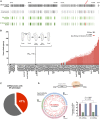
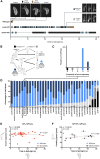
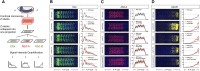
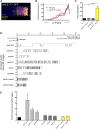
The effects of microRNA (miRNA) regulation on the genetic programs underlying behavior remain largely unexplored. Despite this, recent work in Drosophila shows that mutation of a single miRNA locus (miR-iab4/iab8) affects the capacity of the larva to correct its orientation if turned upside down (self-righting, SR), suggesting that other miRNAs might also be involved in behavioral control. Here we explore this possibility, studying early larval SR behavior in a collection of 81 Drosophila miRNA mutants covering almost the entire miRNA complement of the late embryo. Unexpectedly, we observe that >40% of all miRNAs tested significantly affect SR time, revealing pervasive behavioral effects of miRNA regulation in the early larva. Detailed analyses of those miRNAs affecting SR behavior (SR-miRNAs) show that individual miRNAs can affect movement in different ways, suggesting that specific molecular and cellular elements are affected by individual miRNA mutations. Furthermore, gene expression analysis shows that the Hox gene Abdominal-B (Abd-B) represents one of the targets deregulated by several SR-miRNAs. Our work thus reveals pervasive effects of miRNA regulation on a complex innate behavior in Drosophila and suggests that miRNAs may be core components of the genetic programs underlying behavioral control in other animals too.
Keywords: CNS; Drosophila; Hox genes; behavior; miRNA regulation; microRNA; nervous system.
Copyright © 2017 Picao-Osorio et al.
Figures
References
-
- Allada R., White N. E., So W. V., Hall J. C., Rosbash M., 1998. A mutant Drosophila homolog of mammalian Clock disrupts circadian rhythms and transcription of period and timeless. Cell 93: 791–804. - PubMed
-
- Alonso C. R., 2012. A complex “mRNA degradation code” controls gene expression during animal development. Trends Genet. 28: 78–88. - PubMed
-
- Armstrong J. D., Texada M. J., Munjaal R., Baker D. A., Beckingham K. M., 2006. Gravitaxis in Drosophila melanogaster: a forward genetic screen. Genes Brain Behav. 5: 222–239. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

