The SOS and RpoS Regulons Contribute to Bacterial Cell Robustness to Genotoxic Stress by Synergistically Regulating DNA Polymerase Pol II
- PMID: 28468910
- PMCID: PMC5500135
- DOI: 10.1534/genetics.116.199471
The SOS and RpoS Regulons Contribute to Bacterial Cell Robustness to Genotoxic Stress by Synergistically Regulating DNA Polymerase Pol II
Abstract
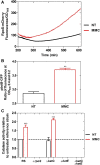
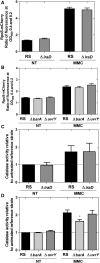
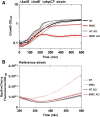
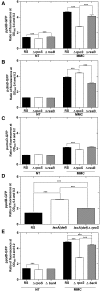
Mitomycin C (MMC) is a genotoxic agent that induces DNA cross-links, DNA alkylation, and the production of reactive oxygen species (ROS). MMC induces the SOS response and RpoS regulons in Escherichia coli SOS-encoded functions are required for DNA repair, whereas the RpoS regulon is typically induced by metabolic stresses that slow growth. Thus, induction of the RpoS regulon by MMC may be coincidental, because DNA damage slows growth; alternatively, the RpoS regulon may be an adaptive response contributing to cell survival. In this study, we show that the RpoS regulon is primarily induced by MMC-induced ROS production. We also show that RpoS regulon induction is required for the survival of MMC-treated growing cells. The major contributor to RpoS-dependent resistance to MMC treatment is DNA polymerase Pol II, which is encoded by the polB gene belonging to the SOS regulon. The observation that polB gene expression is controlled by the two major stress response regulons that are required to maximize survival and fitness further emphasizes the key role of this DNA polymerase as an important factor in genome stability.
Keywords: DNA polymerase II; Escherichia coli; RpoS; SOS; mitomycin C.
Copyright © 2017 by the Genetics Society of America.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The Escherichia coli SOS gene sbmC is regulated by H-NS and RpoS during the SOS induction and stationary growth phase.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2001 Nov 9;288(4):1052-8. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.2001.5872. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2001. PMID: 11689018
-
A DNA damage response in Escherichia coli involving the alternative sigma factor, RpoS.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2009 Jan 13;106(2):611-6. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0803665106. Epub 2009 Jan 5. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2009. PMID: 19124769 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of genetic factors altering the SOS induction of DNA damage-inducible yebG gene in Escherichia coli.FEMS Microbiol Lett. 1999 Aug 15;177(2):271-7. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6968.1999.tb13743.x. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 1999. PMID: 10474193
-
The two-component network and the general stress sigma factor RpoS (sigma S) in Escherichia coli.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2008;631:40-53. doi: 10.1007/978-0-387-78885-2_4. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2008. PMID: 18792681 Review.
-
Proteolysis of sigmaS (RpoS) and the general stress response in Escherichia coli.Res Microbiol. 2009 Nov;160(9):667-76. doi: 10.1016/j.resmic.2009.08.014. Epub 2009 Sep 16. Res Microbiol. 2009. PMID: 19765651 Review.
Cited by
-
PsrA Regulator Connects Cell Physiology and Class 1 Integron Integrase Gene Expression Through the Regulation of lexA Gene Expression in Pseudomonas spp.Curr Microbiol. 2019 Mar;76(3):320-328. doi: 10.1007/s00284-019-01626-7. Epub 2019 Jan 25. Curr Microbiol. 2019. PMID: 30684026
-
Insights into antibiotic resistance promoted by quinolone exposure.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2025 Jan 31;69(1):e0099724. doi: 10.1128/aac.00997-24. Epub 2024 Nov 26. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2025. PMID: 39589140 Free PMC article.
-
Asymmetric chromosome segregation and cell division in DNA damage-induced bacterial filaments.Mol Biol Cell. 2020 Dec 15;31(26):2920-2931. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E20-08-0547. Epub 2020 Oct 28. Mol Biol Cell. 2020. PMID: 33112716 Free PMC article.
-
The major contribution of the DNA damage-triggered reactive oxygen species production to cell death: implications for antimicrobial and cancer therapy.Curr Genet. 2018 Jun;64(3):567-569. doi: 10.1007/s00294-017-0787-3. Epub 2017 Nov 27. Curr Genet. 2018. PMID: 29181628 Review.
-
Directed evolution of Escherichia coli with lower-than-natural plasmid mutation rates.Nucleic Acids Res. 2018 Sep 28;46(17):9236-9250. doi: 10.1093/nar/gky751. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018. PMID: 30137492 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ali-Osman F., Rairkar A., Young P., 1995. Formation and repair of 1,3-bis-(2-chloroethyl)-1-nitrosourea and cisplatin induced total genomic DNA interstrand crosslinks in human glioma cells. Cancer Biochem. Biophys. 14: 231–241. - PubMed
-
- Bouveret E., Battesti A. E., 2011. The stringent response. in Bacterial Stress Responses, edited by Storz G., Hengge R. ASM Press, Washington, DC.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

