Dominant ER Stress-Inducing WFS1 Mutations Underlie a Genetic Syndrome of Neonatal/Infancy-Onset Diabetes, Congenital Sensorineural Deafness, and Congenital Cataracts
- PMID: 28468959
- PMCID: PMC5482085
- DOI: 10.2337/db16-1296
Dominant ER Stress-Inducing WFS1 Mutations Underlie a Genetic Syndrome of Neonatal/Infancy-Onset Diabetes, Congenital Sensorineural Deafness, and Congenital Cataracts
Abstract
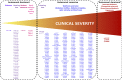
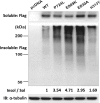
Neonatal diabetes is frequently part of a complex syndrome with extrapancreatic features: 18 genes causing syndromic neonatal diabetes have been identified to date. There are still patients with neonatal diabetes who have novel genetic syndromes. We performed exome sequencing in a patient and his unrelated, unaffected parents to identify the genetic etiology of a syndrome characterized by neonatal diabetes, sensorineural deafness, and congenital cataracts. Further testing was performed in 311 patients with diabetes diagnosed before 1 year of age in whom all known genetic causes had been excluded. We identified 5 patients, including the initial case, with three heterozygous missense mutations in WFS1 (4/5 confirmed de novo). They had diabetes diagnosed before 12 months (2 before 6 months) (5/5), sensorineural deafness diagnosed soon after birth (5/5), congenital cataracts (4/5), and hypotonia (4/5). In vitro studies showed that these WFS1 mutations are functionally different from the known recessive Wolfram syndrome-causing mutations, as they tend to aggregate and induce robust endoplasmic reticulum stress. Our results establish specific dominant WFS1 mutations as a cause of a novel syndrome including neonatal/infancy-onset diabetes, congenital cataracts, and sensorineural deafness. This syndrome has a discrete pathophysiology and differs genetically and clinically from recessive Wolfram syndrome.
© 2017 by the American Diabetes Association.
Figures



References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

