Genetic Disruption of Adenosine Kinase in Mouse Pancreatic β-Cells Protects Against High-Fat Diet-Induced Glucose Intolerance
- PMID: 28468960
- PMCID: PMC5482077
- DOI: 10.2337/db16-0816
Genetic Disruption of Adenosine Kinase in Mouse Pancreatic β-Cells Protects Against High-Fat Diet-Induced Glucose Intolerance
Erratum in
-
Erratum. Genetic Disruption of Adenosine Kinase in Mouse Pancreatic β-Cells Protects Against High-Fat Diet-Induced Glucose Intolerance. Diabetes 2017;66:1928-1938.Diabetes. 2017 Dec;66(12):3145. doi: 10.2337/db17-er12f. Epub 2017 Oct 10. Diabetes. 2017. PMID: 29017999 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
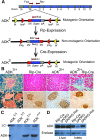
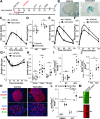
Islet β-cells adapt to insulin resistance through increased insulin secretion and expansion. Type 2 diabetes typically occurs when prolonged insulin resistance exceeds the adaptive capacity of β-cells. Our prior screening efforts led to the discovery that adenosine kinase (ADK) inhibitors stimulate β-cell replication. Here, we evaluated whether ADK disruption in mouse β-cells affects β-cell mass and/or protects against high-fat diet (HFD)-induced glucose dysregulation. Mice targeted at the Adk locus were bred to Rip-Cre and Ins1-Cre/ERT1Lphi mice to enable constitutive (βADKO) and conditional (iβADKO) disruption of ADK expression in β-cells, respectively. Weight gain, glucose tolerance, insulin sensitivity, and glucose-stimulated insulin secretion (GSIS) were longitudinally monitored in normal chow (NC)-fed and HFD-fed mice. In addition, β-cell mass and replication were measured by immunofluorescence-based islet morphometry. NC-fed adult βADKO and iβADKO mice displayed glucose tolerance, insulin tolerance and β-cell mass comparable to control animals. By contrast, HFD-fed βADKO and iβADKO animals had improved glucose tolerance and increased in vivo GSIS. Improved glucose handling was associated with increased β-cell replication and mass. We conclude that ADK expression negatively regulates the adaptive β-cell response to HFD challenge. Therefore, modulation of ADK activity is a potential strategy for enhancing the adaptive β-cell response.
© 2017 by the American Diabetes Association.
Figures



References
-
- Weir GC, Bonner-Weir S. Five stages of evolving beta-cell dysfunction during progression to diabetes. Diabetes 2004;53(Suppl. 3):S16–S21 - PubMed
-
- Butler AE, Janson J, Bonner-Weir S, Ritzel R, Rizza RA, Butler PC. Beta-cell deficit and increased beta-cell apoptosis in humans with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes 2003;52:102–110 - PubMed
-
- Jonas JC, Sharma A, Hasenkamp W, et al. Chronic hyperglycemia triggers loss of pancreatic beta cell differentiation in an animal model of diabetes. J Biol Chem 1999;274:14112–14121 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

