Exploiting pH-Regulated Dimer-Tetramer Transformation of Concanavalin A to Develop Colorimetric Biosensing of Bacteria
- PMID: 28469128
- PMCID: PMC5431225
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-017-01371-6
Exploiting pH-Regulated Dimer-Tetramer Transformation of Concanavalin A to Develop Colorimetric Biosensing of Bacteria
Abstract
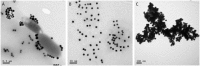
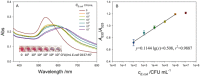
Gold nanoparticles (AuNPs) aggregation-based colorimetric biosensing remains a challenge for bacteria due to their large size. Here we propose a novel colorimetric biosensor for rapid detection of Escherichia coli O157:H7 (E. coli O157:H7) in milk samples based on pH-regulated transformation of dimer/tetramer of Concanavalin A (Con A) and the Con A-glycosyl recognition. Briefly, antibody-modified magnetic nanoparticles was used to capture and concentrate E. coli O157:H7 and then to label with Con A; pH adjusted to 5 was then applied to dissociate Con A tetramer to release dimer, which was collected and re-formed tetramer at pH of 7 to cause the aggregation of dextran-modified AuNPs. The interesting pH-dependent conformation-transformation behavior of Con A innovated the design of the release from the bacteria surface and then the reconstruction of Con A. Therefore, we realized the sensitive colorimetric biosensing of bacteria, which are much larger than AuNPs that is generally not suitable for this kind of method. The proposed biosensor exhibited a limit of detection down to 41 CFU/mL, short assay time (~95 min) and satisfactory specificity. The biosensor also worked well for the detection in milk sample, and may provide a universal concept for the design of colorimetric biosensors for bacteria and virus.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures




Similar articles
-
An integrated magnetic separation enzyme-linked colorimetric sensing platform for field detection of Escherichia coli O157: H7 in food.Mikrochim Acta. 2024 Jul 8;191(8):454. doi: 10.1007/s00604-024-06497-9. Mikrochim Acta. 2024. PMID: 38976069
-
Paper-based magnetic nanoparticle-peptide probe for rapid and quantitative colorimetric detection of Escherichia coli O157:H7.Biosens Bioelectron. 2017 Jun 15;92:702-708. doi: 10.1016/j.bios.2016.10.023. Epub 2016 Oct 10. Biosens Bioelectron. 2017. PMID: 27839734
-
A microfluidic colorimetric biosensor for rapid detection of Escherichia coli O157:H7 using gold nanoparticle aggregation and smart phone imaging.Biosens Bioelectron. 2019 Jan 15;124-125:143-149. doi: 10.1016/j.bios.2018.10.006. Epub 2018 Oct 11. Biosens Bioelectron. 2019. PMID: 30366259
-
Electrochemical biosensors for rapid detection of Escherichia coli O157:H7.Talanta. 2017 Jan 1;162:511-522. doi: 10.1016/j.talanta.2016.10.050. Epub 2016 Oct 12. Talanta. 2017. PMID: 27837864 Review.
-
Gold nanoparticle-based colorimetric biosensors.Nanoscale. 2017 Dec 21;10(1):18-33. doi: 10.1039/c7nr06367a. Nanoscale. 2017. PMID: 29211091 Review.
Cited by
-
Lignin nanoparticles are renewable and functional platforms for the concanavalin a oriented immobilization of glucose oxidase-peroxidase in cascade bio-sensing.RSC Adv. 2020 Aug 5;10(48):29031-29042. doi: 10.1039/d0ra04485g. eCollection 2020 Aug 3. RSC Adv. 2020. PMID: 35520043 Free PMC article.
-
Highly sensitive Escherichia coli detection via cell surface in situ cytocompatible ATRP.Anal Bioanal Chem. 2025 Sep;417(22):4991-5000. doi: 10.1007/s00216-025-06017-5. Epub 2025 Jul 25. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2025. PMID: 40711561
-
A comprehensive review of transduction methods of lectin-based biosensors in biomedical applications.Heliyon. 2024 Sep 24;10(19):e38371. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e38371. eCollection 2024 Oct 15. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 39386779 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nanomaterial application in bio/sensors for the detection of infectious diseases.Talanta. 2021 Aug 1;230:122026. doi: 10.1016/j.talanta.2020.122026. Epub 2020 Dec 17. Talanta. 2021. PMID: 33934756 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Rapid naked-eye detection of Gram-positive bacteria by vancomycin-based nano-aggregation.RSC Adv. 2018 Jul 12;8(44):25094-25103. doi: 10.1039/c8ra03540g. eCollection 2018 Jul 9. RSC Adv. 2018. PMID: 35542172 Free PMC article.
References
-
- World Health Organization. Food safety. http://www.who.int/mediacentre/factsheets/fs399/en/ (2015).
-
- Chen L, et al. Heterogemini surfactant assisted synthesis of monodisperse icosahedral gold nanocrystals and their applications in electrochemical biosensing. RSC Adv. 2016;6:31301–31307. doi: 10.1039/C6RA03348B. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

