Real-Time Reverse-Transcription Quantitative Polymerase Chain Reaction Assay Is a Feasible Method for the Relative Quantification of Heregulin Expression in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Tissue
- PMID: 28469400
- PMCID: PMC5391987
- DOI: 10.1177/1177271917699850
Real-Time Reverse-Transcription Quantitative Polymerase Chain Reaction Assay Is a Feasible Method for the Relative Quantification of Heregulin Expression in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Tissue
Abstract
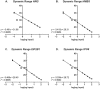
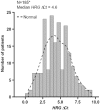
In preclinical studies, heregulin (HRG) expression was shown to be the most relevant predictive biomarker for response to patritumab, a fully human anti-epidermal growth factor receptor 3 monoclonal antibody. In support of a phase 2 study of erlotinib ± patritumab in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC), a reverse-transcription quantitative polymerase chain reaction (RT-qPCR) assay for relative quantification of HRG expression from formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded (FFPE) NSCLC tissue samples was developed and validated and described herein. Test specimens included matched FFPE normal lung and NSCLC and frozen NSCLC tissue, and HRG-positive and HRG-negative cell lines. Formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded tissue was examined for functional performance. Heregulin distribution was also analyzed across 200 NSCLC commercial samples. Applied Biosystems TaqMan Gene Expression Assays were run on the Bio-Rad CFX96 real-time PCR platform. Heregulin RT-qPCR assay specificity, PCR efficiency, PCR linearity, and reproducibility were demonstrated. The final assay parameters included the Qiagen FFPE RNA Extraction Kit for RNA extraction from FFPE NSCLC tissue, 50 ng of RNA input, and 3 reference (housekeeping) genes (HMBS, IPO8, and EIF2B1), which had expression levels similar to HRG expression levels and were stable among FFPE NSCLC samples. Using the validated assay, unimodal HRG distribution was confirmed across 185 evaluable FFPE NSCLC commercial samples. Feasibility of an RT-qPCR assay for the quantification of HRG expression in FFPE NSCLC specimens was demonstrated.
Keywords: Real-time reverse-transcription polymerase chain reaction (RT-qPCR); heregulin; non/small cell lung cancer; validation.
Conflict of interest statement
DECLARATION OF CONFLICTING INTERESTS: The author(s) declared the following potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article: JK and KS are former employees of MolecularMD. XJ, RAB, and DF are former employees of Daiichi Sankyo Pharma Development. WF is an employee of Daiichi Sankyo Pharma Development. KN is an employee of Daiichi Sankyo Co., Ltd. MS was an employee of U3 Pharma GmbH. CS is an employee of MolecularMD.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Clinical Translation and Validation of a Predictive Biomarker for Patritumab, an Anti-human Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor 3 (HER3) Monoclonal Antibody, in Patients With Advanced Non-small Cell Lung Cancer.EBioMedicine. 2015 Feb 12;2(3):264-71. doi: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2015.02.005. eCollection 2015 Mar. EBioMedicine. 2015. PMID: 26137564 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Technical validation of an RT-qPCR in vitro diagnostic test system for the determination of breast cancer molecular subtypes by quantification of ERBB2, ESR1, PGR and MKI67 mRNA levels from formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded breast tumor specimens.BMC Cancer. 2016 Jul 7;16:398. doi: 10.1186/s12885-016-2476-x. BMC Cancer. 2016. PMID: 27389414 Free PMC article.
-
Circulating heregulin level is associated with the efficacy of patritumab combined with erlotinib in patients with non-small cell lung cancer.Lung Cancer. 2017 Mar;105:1-6. doi: 10.1016/j.lungcan.2016.12.018. Epub 2017 Jan 9. Lung Cancer. 2017. PMID: 28236978 Clinical Trial.
-
Intracranial meningiomas, the VEGF-A pathway, and peritumoral brain oedema.Dan Med J. 2013 Apr;60(4):B4626. Dan Med J. 2013. PMID: 23651727 Review.
-
Immunocytochemistry of cytology specimens for predictive biomarkers in lung cancer.Transl Lung Cancer Res. 2020 Jun;9(3):898-905. doi: 10.21037/tlcr.2019.12.31. Transl Lung Cancer Res. 2020. PMID: 32676355 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Optimization of internal reference genes for qPCR in human pancreatic cancer research.Transl Cancer Res. 2020 Apr;9(4):2962-2971. doi: 10.21037/tcr.2020.02.48. Transl Cancer Res. 2020. PMID: 35117652 Free PMC article.
-
Expression of FXR and HRG and their clinicopathological significance in benign and malignant pancreatic lesions.Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2019 Jun 1;12(6):2111-2120. eCollection 2019. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2019. PMID: 31934033 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2015. CA Cancer J Clin. 2015;65:5–29. - PubMed
-
- National Comprehensive Cancer Network (NCCN). Clinical Practice Guidelines in Oncology (NCCN Guidelines) Non-small cell lung cancer. Version 4. http://www.nccn.org. Published 2016. Accessed September 1, 2016.
-
- Garon EB, Rizvi NA, Hui R, et al. ; KEYNOTE-001 Investigators. Pembrolizumab for the treatment of non–small-cell lung cancer. N Engl J Med. 2015;372:2018–2028. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

