Cellular and Molecular Underpinnings of Neuronal Assembly in the Central Auditory System during Mouse Development
- PMID: 28469562
- PMCID: PMC5395578
- DOI: 10.3389/fncir.2017.00018
Cellular and Molecular Underpinnings of Neuronal Assembly in the Central Auditory System during Mouse Development
Abstract
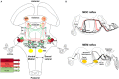
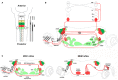
During development, the organization of the auditory system into distinct functional subcircuits depends on the spatially and temporally ordered sequence of neuronal specification, differentiation, migration and connectivity. Regional patterning along the antero-posterior axis and neuronal subtype specification along the dorso-ventral axis intersect to determine proper neuronal fate and assembly of rhombomere-specific auditory subcircuits. By taking advantage of the increasing number of transgenic mouse lines, recent studies have expanded the knowledge of developmental mechanisms involved in the formation and refinement of the auditory system. Here, we summarize several findings dealing with the molecular and cellular mechanisms that underlie the assembly of central auditory subcircuits during mouse development, focusing primarily on the rhombomeric and dorso-ventral origin of auditory nuclei and their associated molecular genetic pathways.
Keywords: DV molecular determinants; Hox genes; central auditory system; mouse lineage tracing; rhombomeres.
Figures





References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

