Plant-Produced Asialo-Erythropoietin Restores Pancreatic Beta-Cell Function by Suppressing Mammalian Sterile-20-like Kinase (MST1) and Caspase-3 Activation
- PMID: 28469576
- PMCID: PMC5395651
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2017.00208
Plant-Produced Asialo-Erythropoietin Restores Pancreatic Beta-Cell Function by Suppressing Mammalian Sterile-20-like Kinase (MST1) and Caspase-3 Activation
Abstract
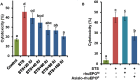
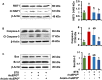
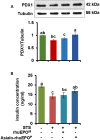
Pancreatic beta-cell death adversely contributes to the progression of both type I and II diabetes by undermining beta-cell mass and subsequently diminishing endogenous insulin production. Therapeutics to impede or even reverse the apoptosis and dysfunction of beta-cells are urgently needed. Asialo-rhuEPO, an enzymatically desialylated form of recombinant human erythropoietin (rhuEPO), has been shown to have cardioprotective and neuroprotective functions but with no adverse effects like that of sialylated rhuEPO. Heretofore, the anti-apoptotic effect of asialo-rhuEPO on pancreatic beta-cells has not been reported. In the current study, we investigated the cytoprotective properties of plant-produced asialo-rhuEPO (asialo-rhuEPOP) against staurosporine-induced cell death in the pancreatic beta-cell line RIN-m5F. Our results showed that 60 IU/ml asialo-rhuEPOP provided 41% cytoprotection while 60 IU/ml rhuEPO yielded no effect. Western blotting results showed that asialo-rhuEPOP treatment inhibited both MST1 and caspase-3 activation with the retention of PDX1 and insulin levels close to untreated control cells. Our study provides the first evidence indicating that asialo-rhuEPOP-mediated protection involves the reduction of MST1 activation, which is considered a key mediator of apoptotic signaling in beta-cells. Considering the many advantages its plant-based expression, asialo-rhuEPOP could be potentially developed as a novel and inexpensive agent to treat or prevent diabetes after further performing studies in cell-based and animal models of diabetes.
Keywords: MST1; asialo-rhuEPO; cytoprotection; insulin secretion; pancreatic beta-cell death.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Recombinant asialoerythropoetin protects HL-1 cardiomyocytes from injury via suppression of Mst1 activation.Biochem Biophys Rep. 2019 Jan 9;17:157-168. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrep.2019.01.004. eCollection 2019 Mar. Biochem Biophys Rep. 2019. PMID: 30671548 Free PMC article.
-
Cytoprotective effect of recombinant human erythropoietin produced in transgenic tobacco plants.PLoS One. 2013 Oct 4;8(10):e76468. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0076468. eCollection 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 24124563 Free PMC article.
-
Asialo-rhuEPO as a Potential Neuroprotectant for Ischemic Stroke Treatment.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2023 Apr 18;16(4):610. doi: 10.3390/ph16040610. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37111367 Free PMC article. Review.
-
N-Glycosylation engineering of tobacco plants to produce asialoerythropoietin.Plant Cell Rep. 2012 Jul;31(7):1233-43. doi: 10.1007/s00299-012-1244-x. Epub 2012 Feb 28. Plant Cell Rep. 2012. PMID: 22371257
-
MST1: a promising therapeutic target to restore functional beta cell mass in diabetes.Diabetologia. 2016 Sep;59(9):1843-9. doi: 10.1007/s00125-016-3892-9. Epub 2016 Apr 6. Diabetologia. 2016. PMID: 27053234 Review.
Cited by
-
A Novel Plant-Produced Asialo-rhuEPO Protects Brain from Ischemic Damage Without Erythropoietic Action.Transl Stroke Res. 2022 Apr;13(2):338-354. doi: 10.1007/s12975-021-00943-z. Epub 2021 Sep 22. Transl Stroke Res. 2022. PMID: 34553324 Free PMC article.
-
Glycoengineering tobacco plants to stably express recombinant human erythropoietin with different N-glycan profiles.Int J Biol Macromol. 2020 Aug 15;157:158-169. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2020.04.199. Epub 2020 Apr 26. Int J Biol Macromol. 2020. PMID: 32348856 Free PMC article.
-
Functional Analysis of Mature Activin A Produced by Enterokinase in Plant Cells.Rice (N Y). 2025 Mar 14;18(1):16. doi: 10.1186/s12284-025-00775-7. Rice (N Y). 2025. PMID: 40082306 Free PMC article.
-
Recombinant asialoerythropoetin protects HL-1 cardiomyocytes from injury via suppression of Mst1 activation.Biochem Biophys Rep. 2019 Jan 9;17:157-168. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrep.2019.01.004. eCollection 2019 Mar. Biochem Biophys Rep. 2019. PMID: 30671548 Free PMC article.
-
Apoptosis in Type 2 Diabetes: Can It Be Prevented? Hippo Pathway Prospects.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Jan 7;23(2):636. doi: 10.3390/ijms23020636. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35054822 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Akiyoshi H., Nakaya Y. (2000). Effect of PKC on glucose-mediated insulin secretion in HIT-T15 cells. JOP 1 49–57. - PubMed
-
- America’s Biopharmaceutical Research Companies (2014). Medicines in Development for Diabetes, 2014 Report. Available at: http://www.phrma.org/sites/default/files/pdf/diabetes2014.pdf [accessed April 15 2017].
-
- Bennett C. L., Silver S. M., Samaras A. T., Blau C. A., Gleason K. J., Barnato S. E., et al. (2008). Venous thromboembolism and mortality associated with recombinant erythropoietin and darbepoetin administration for the treatment of cancer-associated anemia. JAMA 299 914–924. 10.1001/jama.299.8.914 - DOI - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

