Molecular Taxonomy of Sporadic Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis Using Disease-Associated Genes
- PMID: 28469596
- PMCID: PMC5395696
- DOI: 10.3389/fneur.2017.00152
Molecular Taxonomy of Sporadic Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis Using Disease-Associated Genes
Abstract
Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) is a fatal neurodegenerative disease characterized by selective loss of upper and lower motor neurons. Despite intensive research, the origin and progression of ALS remain largely unknown, suggesting that the traditional clinical diagnosis and treatment strategies might not be adequate to completely capture the molecular complexity underlying the disease. In our previous work, comprehensive genomic profiling of 41 motor cortex samples enabled to discriminate control from sporadic ALS patients and segregated these latter into two distinct subgroups, each associated with different deregulated genes and pathways. Interestingly, some deregulated genes in sporadic ALS were previously associated with familiar ALS, indicating shared pathogenic mechanisms between the two forms of disease. In this, we performed cluster analysis on the same whole-genome expression profiles using a restricted (203) subset of genes extensively implicated in monogenic forms of ALS. Surprisingly, this short and unbiased gene list was sufficiently representative to allow the accurate separation of SALS patients from controls and the stratification of SALS patients into two molecularly distinct subgroups. Overall, our findings support the existence of a molecular taxonomy for ALS and represent a further step toward the establishment of a molecular-based diagnosis and patient-tailored therapies.
Keywords: amyotrophic lateral sclerosis; expression profiling; gene ontology analysis; genomics; molecular classification of disease subtypes.
Figures
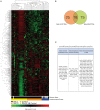
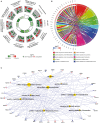

References
-
- Ravits J, Appel S, Baloh RH, Barohn R, Brooks BR, Elman L, et al. Deciphering amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: what phenotype, neuropathology and genetics are telling us about pathogenesis. Amyotroph Lateral Scler Frontotemporal Degener (2013) 14(Suppl 1):5–18. 10.3109/21678421.2013.778548 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

